
Fly Local Sensitive Hashing (FLSH) is a biomimetic data-independent hashing method inspired by the mechanism of odor processing system in drosophila. In this paper,we propose a novel Randomized Sampling-based Fly Local Sensitive Hashing (rs-FLSH) to model the randomness occurred during the establishment of synapses between neurons.Significant performance improvement can be achieved by applying a novel randomized sampling scheme in rs-FLSH,in which the sample rate is modeled by a Gaussian random variable rather than a fixed value in FLSH.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Alternating autoencoders for matrix completion
- Log in to post comments
We consider autoencoders (AEs) for matrix completion (MC) with application to collaborative filtering (CF) for recommedation systems. It is observed that for a given sparse user-item rating matrix, denoted asM, an AE performs matrix factorization so that the recovered matrix is represented as a product of user and item feature matrices.
Poster_Lee.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Profit Maximizing Logistic Regression Modeling for Credit Scoring
- Log in to post comments
Multiple classification techniques have been employed for different business applications. In the particular case of credit scoring, a classifier which maximizes the total profit is preferable. The recently proposed expected maximum profit (EMP) measure for credit scoring allows to select the most profitable classifier. Taking the idea of the EMP one step further, it is desirable to integrate the measure into model construction, and thus obtain a profit maximizing model.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views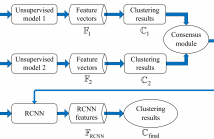
- Read more about PSEUDO-SUPERVISED APPROACH FOR TEXT CLUSTERING BASED ON CONSENSUS ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, neural networks (NN) have achieved remarkable
performance improvement in text classification due to
their powerful ability to encode discriminative features by
incorporating label information into model training. Inspired
by the success of NN in text classification, we propose a
pseudo-supervised neural network approach for text clustering.
The neural network is trained in a supervised fashion
with pseudo-labels, which are provided by the cluster labels
of pre-clustering on unsupervised document representations.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about SPS Malaysia Chapter Member-Driven Initiative: Professional Knowledge Transfer Workshop 2017: Arduino Simple Programming
- Log in to post comments
Winter 2017 Seasonal School Workshop, Malaysia. The Arduino Simple Programming at school was held at five different schools near Parit Raja, Batu Pahat, Johor from October-November 2017. The schools are SK Jelutong, SMK Sri gading, SK Pintas Puding, SK Bukit Kuari and SK Seri Sabak Uni. The objective of Professional Knowledge Transfer Workshop is to give an exposure to the students of primary and secondary schools on engineering and to inspire them to be engineers. This program was organized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) UTHM Student Branch with cooperation of IEEE Signal Processing Society (SPS) Malaysia Chapter. The program is fully funded by IEEE Signal Processing Society (SPS) under the IEEE SPS Member-Driven Initiative Program with the amount of USD 1,400. The fund had been used to buy 30 Arduino Uno kits, purchasing stationery, and refreshments for 30 students from each school, 10 postgraduate students from UTHM IEEE student branch and 13 Academic staff from FKEE, UTHM.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views- Read more about Automatic Question-answering Using a Deep Similarity Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
Automatic question-answering is a classical problem in natural language processing, which aims at designing systems that can automatically answer a question, in the same way as human does. In this work, we propose a deep learning based model for automatic question-answering. First the questions and answers are embedded using neural probabilistic modeling. Then a deep similarity neural network is trained to find the similarity score of a pair of answer and question. Then for each question, the best answer is found as the one with the highest similarity score.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 ViewsWe solve the compressive sensing problem via convolutional factor analysis, where the convolutional dictionaries are learned in situ from the compressed measurements. An alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) paradigm for compressive sensing inversion based on convolutional factor analysis is developed. The proposed algorithm provides reconstructed images as well as features, which can be directly used for recognition (e:g:, classification) tasks.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views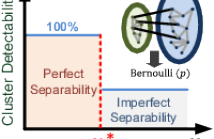
- Read more about AMOS: An Automated Model Order Selection Algorithm for Spectral Graph Clustering
- Log in to post comments
One of the longstanding problems in spectral graph clustering (SGC) is the so-called model order selection problem: automated selection of the correct number of clusters. This is equivalent to the problem of finding the number of connected components or communities in an undirected graph. In this paper, we propose AMOS, an automated model order selection algorithm for SGC.
- Categories:
 113 Views
113 Views
- Read more about Towards Building a Standard Dataset for Arabic Keyphrase Extraction Evaluation
- Log in to post comments
Keyphrases are short phrases that best represent a document content. They can be useful in a variety of applications, including document summarization and retrieval models. In this paper, we introduce the first dataset of keyphrases for an Arabic document collection, obtained by means of crowdsourcing. We experimentally evaluate different crowdsourced answer aggregation strategies and validate their performances against expert annotations to evaluate the quality of our dataset. We report about our experimental results, the dataset features, some lessons learned, and ideas for future
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views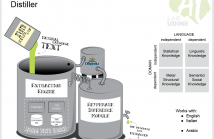
- Read more about Leveraging Arabic Morphology and Syntax for Achieving Better Keyphrase Extraction
- Log in to post comments
Arabic is one of the fastest growing languages on the Web, with an increasing amount of user generated content being published by both native and non-native speakers all over the world. Despite the great linguistic differences between Arabic and western languages such as English, most Arabic keyphrase extraction systems rely on approaches designed for western languages, thus ignoring its rich morphology and syntax. In this paper we present a new approach leveraging the Arabic morphology and syntax to generate a restricted set of meaningful candidates among which keyphrases are selected.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views