
- Read more about Decompressing Lempel-Ziv compressed text
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of decompressing the Lempel--Ziv 77 representation of a string $S$ of length $n$ using a working space as close as possible to the size $z$ of the input. The folklore solution for the problem runs in $O(n)$ time but requires random access to the whole decompressed text. Another folklore solution is to convert LZ77 into a grammar of size $O(z\log(n/z))$ and then stream $S$ in linear time. In this paper, we show that $O(n)$ time and $O(z)$ working space can be achieved for constant-size alphabets.
- Categories:
 133 Views
133 Views
- Read more about Approximating Optimal Bidirectional Macro Schemes.
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Lempel-Ziv is an easy-to-compute member of a wide family of so-called macro schemes; it restricts pointers to go in one direction only. Optimal bidirectional macro schemes are NP-complete to find, but they may provide much better compression on highly repetitive sequences. We consider the problem of approximating optimal bidirectional macro schemes. We describe a simulated annealing algorithm that usually converges quickly. Moreover, in some cases, we obtain bidirectional macro schemes that are provably a 2-approximation of the optimal.
- Categories:
 121 Views
121 Views
- Read more about Grammar compression with probabilistic context-free grammar
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
We propose a new approach for universal lossless text compression, based on grammar compression. In the literature, a target string T has been compressed as a context-free grammar G in Chomsky normal form satisfying L(G) = T. Such a grammar is often called a straight-line program (SLP). In this work, we consider a probabilistic grammar G that generates T, but not necessarily as a unique element of L(G). In order to recover the original text T unambiguously, we keep both the grammar G and the derivation tree of T from the start symbol in G, in compressed form.
dcc_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 111 Views
111 Views
- Read more about Reverse Multi-Delimiter Compression Codes
- Log in to post comments
An enhanced version of a recently introduced family of variable length binary codes with multiple pattern delimiters is presented and discussed. These codes are complete, universal, synchronizable, they have monotonic indexing and allow a standard search in compressed files. Comparing the compression rate on natural language texts demonstrates that introduced codes appear to be much superior to other known codes with similar properties. A fast byte-aligned decoding algorithm is constructed, which operates much faster than the one for Fibonacci codes.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about An Accurate Evaluation of MSD Log-likelihood and its Application in Human Action Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we examine the problem of modeling overdispersed frequency vectors that are naturally generated by several machine learning and computer vision applications.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about An Accurate Evaluation of MSD Log-likelihood and its Application in Human Action Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we examine the problem of modeling overdispersed frequency vectors that are naturally generated by several machine learning and computer vision applications.
MSD_Mesh.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
In this research, we aim to propose a data preprocessing framework particularly for financial sector to generate the rating data as input to the collaborative system. First, clustering technique is applied to cluster all users based on their demographic information which might be able to differentiate the customers’ background. Then, for each customer group, the importance of demographic characteristics which are highly associated with financial products purchasing are analyzed by the proposed fuzzy integral technique.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views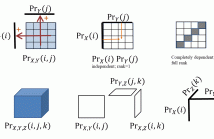
- Read more about GlobalSIP 2018 Keynote: Tensors and Probability: An Intriguing Union (N. Sidiropoulos, N. Kargas, X. Fu)
- Log in to post comments
We reveal an interesting link between tensors and multivariate statistics. The rank of a multivariate probability tensor can be interpreted as a nonlinear measure of statistical dependence of the associated random variables. Rank equals one when the random variables are independent, and complete statistical dependence corresponds to full rank; but we show that rank as low as two can already model strong statistical dependence.
- Categories:
 111 Views
111 Views
- Read more about Dynamic Network Identification From Non-stationary Vector Autoregressive Time Series
- Log in to post comments
Learning the dynamics of complex systems features a large number of applications in data science. Graph-based modeling and inference underpins the most prominent family of approaches to learn complex dynamics due to their ability to capture the intrinsic sparsity of direct interactions in such systems. They also provide the user with interpretable graphs that unveil behavioral patterns and changes.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views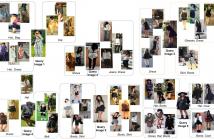
Developing recommendation system for fashion images is challenging due to the inherent ambiguity associated with what criterion a user is looking at. Suggesting multiple images where each output image is similar to the query image on the basis of a different feature or part is one way to mitigate the problem. Existing works for fashion recommendation have used Siamese or Triplet network to learn features between a similar pair and a similar dissimilar triplet respectively.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views