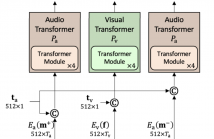
- Read more about ModEFormer: Modality-preserving embedding for audio-video synchronization using transformers
- Log in to post comments
Lack of audio-video synchronization is a common problem during television broadcasts and video conferencing, leading to an unsatisfactory viewing experience. A widely accepted paradigm is to create an error detection mechanism that identifies the cases when audio is leading or lagging. We propose ModEFormer, which independently extracts audio and video embeddings using modality-specific transformers.
- Categories:
 167 Views
167 Views
Recently, cross modal compression (CMC) is proposed to compress highly redundant visual data into a compact, common, human-comprehensible domain (such as text) to preserve semantic fidelity for semantic-related applications. However, CMC only achieves a certain level of semantic fidelity at a constant rate, and the model aims to optimize the probability of the ground truth text but not directly semantic fidelity. To tackle the problems, we propose a novel scheme named rate-distortion optimized CMC (RDO-CMC).
2023003317.pdf
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about Rate-Distortion-Classification Model In Lossy Image Compression
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Rate-distortion (RD) theory is a fundamental theory for lossy image compression that treats compressing the original images to a specified bitrate with minimal signal distortion, which is an essential metric in practical application. Moreover, with the development of visual analysis applications (such as classification, detection, segmentation, etc.), the semantic distortion in compressed images are also an important dimension in the theoretical analysis of lossy image compression.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about Deep Hashing With Hash Center Update for Efficient Image Retrieval
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose an approach for learning binary hash codes
for image retrieval. Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) is used
to design two loss functions for training a neural network such that
the correlation between the two views to CCA is maximum. The
main motivation for using CCA for feature space learning is that
dimensionality reduction is possible and short binary codes could
be generated. The first loss maximizes the correlation between the
hash centers and the learned hash codes. The second loss maximizes
4514-2.pdf
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about TRAINING STRATEGIES FOR AUTOMATIC SONG WRITING: A UNIFIED FRAMEWORK PERSPECTIVE
- Log in to post comments
Automatic song writing (ASW) typically involves four tasks: lyric-to-lyric generation, melody-to-melody generation, lyric-to-melody generation, and melody-to-lyric generation.
Previous works have mainly focused on individual tasks without considering the correlation between them, and thus a unified framework to solve all four tasks has not yet been explored.
ICASSP2022.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about TIME-DOMAIN AUDIO-VISUAL SPEECH SEPARATION ON LOW QUALITY VIDEOS
- Log in to post comments
Incorporating visual information is a promising approach to improve the performance of speech separation. Many related works have been conducted and provide inspiring results. However, low quality videos appear commonly in real scenarios, which may significantly degrade the performance of normal audio-visual speech separation system. In this paper, we propose a new structure to fuse the audio and visual features, which uses the audio feature to select relevant visual features by utilizing the attention mechanism.
poster.pdf
presentation.pptx
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about GLOBAL-LOCAL FEATURE ENHANCEMENT NETWORK FOR ROBUST OBJECT DETECTION USING MMWAVE RADAR AND CAMERA
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about GLOBAL-LOCAL FEATURE ENHANCEMENT NETWORK FOR ROBUST OBJECT DETECTION USING MMWAVE RADAR AND CAMERA
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about COOPNET: MULTI-MODAL COOPERATIVE GENDER PREDICTION IN SOCIAL MEDIA USER PROFILING
- Log in to post comments
icassp poster.pdf
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about TIME-LAG AWARE MULTI-MODAL VARIATIONAL AUTOENCODER USING BASEBALL VIDEOS AND TWEETS FOR PREDICTION OF IMPORTANT SCENES
- Log in to post comments
A novel method based on time-lag aware multi-modal variational autoencoder for prediction of important scenes (Tl-MVAE-PIS) using baseball videos and tweets posted on Twitter is presented in this paper. This paper has the following two technical contributions. First, to effectively use heterogeneous data for the prediction of important scenes, we transform textual, visual and audio features obtained from tweets and videos to the latent features. Then Tl-MVAE-PIS can flexibly express the relationships between them in the constructed latent space.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views