- Read more about FAST: Flow-Assisted Shearlet Transform for Densely-sampled Light Field Reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
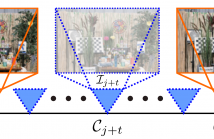
Shearlet Transform (ST) is one of the most effective methods for Densely-Sampled Light Field (DSLF) reconstruction from a Sparsely-Sampled Light Field (SSLF). However, ST requires a precise disparity estimation of the SSLF. To this end, in this paper a state-of-the-art optical flow method, i.e. PWC-Net, is employed to estimate bidirectional disparity maps between neighboring views in the SSLF. Moreover, to take full advantage of optical flow and ST for DSLF reconstruction, a novel learning-based method, referred to as Flow-Assisted Shearlet Transform (FAST), is proposed in this paper.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about AUDIO FEATURE GENERATION FOR MISSING MODALITY PROBLEM IN VIDEO ACTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Despite the recent success of multi-modal action recognition in videos, in reality, we usually confront the situation that some data are not available beforehand, especially for multimodal data. For example, while vision and audio data are required to address the multi-modal action recognition, audio tracks in videos are easily lost due to the broken files or the limitation of devices. To cope with this sound-missing problem, we present an approach to simulating deep audio feature from merely spatial-temporal vision data.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Dynamic Temporal Alignment of Speech to Lips
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Learning Shared Vector Representations of Lyrics and Chords in Music
- Log in to post comments
Music has a powerful influence on a listener's emotions. In this paper, we represent lyrics and chords in a shared vector space using a phrase-aligned chord-and-lyrics corpus. We show that models that use these shared representations predict a listener's emotion while hearing musical passages better than models that do not use these representations. Additionally, we conduct a visual analysis of these learnt shared vector representations and explain how they support existing theories in music.
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views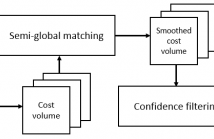
- Read more about Disparity Map Estimation from Cross-modal Stereo
- Log in to post comments
Mono-modal stereo matching problem has been studied for decades. The introduction of cross-modal stereo systems in industrial scene increases the interest in cross-modal stereo matching. The existing algorithms mostly consider mono-modal setting so they do not translate well in cross-modal setting. Recent development for cross-modal stereo considers small local matching and focus mainly on joint enhancement. Therefore, we propose a guided filter-based stereo matching algorithm. It works by integrating guided filter equation in a basic cost function for cost volume generation.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views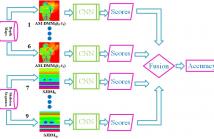
- Read more about CNN-BASED ACTION RECOGNITION USING ADAPTIVE MULTISCALE DEPTH MOTION MAPS AND STABLE JOINT DISTANCE MAPS
- Log in to post comments
Human action recognition has a wide range of applications including biometrics and surveillance. Existing methods mostly focus on a single modality, insufficient to characterize variations among different motions. To address this problem, we present a CNN-based human action recognition framework by fusing depth and skeleton modalities. The proposed Adaptive Multiscale Depth Motion Maps (AM-DMMs) are calculated from depth maps to capture shape, motion cues. Moreover, adaptive temporal windows ensure that AM-DMMs are robust to motion speed variations.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about Can DNNs Learn to Lipread Full Sentences ?
- Log in to post comments
Finding visual features and suitable models for lipreading tasks that are more complex than a well-constrained vocabulary has proven challenging. This paper explores state-of-the-art Deep Neural Network architectures for lipreading based on a Sequence to Sequence Recurrent Neural Network. We report results for both hand-crafted and 2D/3D Convolutional Neural Network visual front-ends, online monotonic attention, and a joint Connectionist Temporal Classification-Sequence-to-Sequence loss.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about ICIP poster presentation Paper TP.P5.2 (1865): 'SHOT SCALE ANALYSIS IN MOVIES BY CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS'
- Log in to post comments
The apparent distance of the camera from the subject of a filmed scene, namely shot scale, is one of the prominent formal features of any filmic product, endowed with both stylistic and narrative functions. In this work we propose to use Convolutional Neural Networks for the automatic classification of shot scale into Close-, Medium-, or Long-shots.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about WATCH, LISTEN ONCE, AND SYNC: AUDIO-VISUAL SYNCHRONIZATION WITH MULTI-MODAL REGRESSION CNN
- Log in to post comments
Recovering audio-visual synchronization is an important task in the field of visual speech processing.
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views- Read more about Bimodal Codebooks Based Adult Video Detection
- Log in to post comments
Multi-modality based adult video detection is an effective approach of filtering pornography. However, existing methods lack accurate representation methods of multi-modality semantics. Addressing at the issue, we propose a novel method of bimodal codebooks based adult video detection. Firstly, the audio codebook is created by periodicity analysis from the labeled audio segments. Secondly, the visual codebook is generated by detecting regions-of-interest (ROI) on the basis of saliency analysis.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views