- Read more about Joint Estimation of the Room Geometry and Modes with Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Acoustical behavior of a room for a given position of microphone and sound source is usually described using the room impulse response. If we rely on the standard uniform sampling, the estimation of room impulse response for arbitrary positions in the room requires a large number of measurements. In order to lower the required sampling rate, some solutions have emerged that exploit the sparse representation of the room wavefield in the terms of plane waves in the low-frequency domain. The plane wave representation has a simple form in rectangular rooms.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about SOURCE AND DIRECTION OF ARRIVAL ESTIMATION BASED ON MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD COMBINED WITH GMM AND EIGENANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
A method is proposed for estimating the source signal and its direction of arrival (DOA) in this paper. It is based on ML estimation of the transfer function between microphones combined with the EM algorithm for a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), assuming that the signal is captured at each microphone with delay corresponding to the traveling of sound and some decay. By this modeling, search for the maximum log-likelihood in the ML estimation can be realized simply by eigenvalue decomposition of a properly designed matrix.
ICASSP2018_B0.pdf
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about Cooperative Tracking using Marginal Diffusion Particle Filters
- Log in to post comments
This paper formulates the general Adapt-then-Combine (ATC) and Random Exchange (RndEx) diffusion filters for an arbitrary nonlinear state-space model. Subsequently, we propose two novel marginal Particle Filter implementations of the general ATC and RndEx filters using respectively a pure Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) strategy and a hybrid Gaussian/SMC methodology. The proposed algorithms are assessed via simulation in a numerical example of cooperative target tracking with received-signal-strength (RSS) sensors.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Distributed Model Construction in Radio Interferometric Calibration
- Log in to post comments
lofar74.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views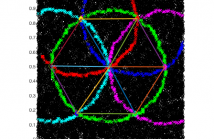
We consider the problem of determining the Euclidean embedding of a dense, planar sensor network. The sensors are equipped with a binary sensing protocol that enables them to detect the neighboring sensors within a fixed radius, R. Using only this connectivity graph, we reconstruct an approximate embedding of the network on an Euclidean plane. To that end, we design an algorithm to identify special landmark nodes in the network whose Euclidean embedding is ``close'' to the vertices of an ideal hexagonal lattice.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about Approximate Support Recovery of Atomic Line Spectral Estimation: A Tale of Resolution and Precision
- Log in to post comments
This work investigates the parameter estimation performance of super-resolution line spectral estimation using atomic norm minimization. The focus is on analyzing the algorithm's accuracy of inferring the frequencies and complex magnitudes from noisy observations. When the Signal-to-Noise Ratio is reasonably high and the true frequencies are separated by $O(\frac{1}{n})$, the atomic norm estimator is shown to localize the correct number of frequencies, each within a neighborhood of size $O(\sqrt{\frac{\log n}{n^3}} \sigma)$ of one of the true frequencies.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about ON THE TRADEOFF BETWEEN RESOLUTION AND AMBIGUITIES FOR NON-UNIFORM LINEAR ARRAYS
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views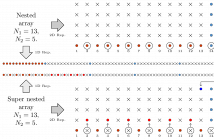
- Read more about Super Nested Arrays: Sparse Arrays with Less Mutual Coupling Than Nested Arrays
- Log in to post comments
In array processing, mutual coupling between sensors has an adverse effect on the estimation of parameters (e.g., DOA). Sparse arrays, such as nested arrays, coprime arrays, and minimum redundancy arrays (MRAs), have reduced mutual coupling compared to uniform linear arrays (ULAs). With $N$ denoting the number of sensors, these sparse arrays offer $O(N^2)$ freedoms for source estimation because their difference coarrays have $O(N^2)$-long ULA segments.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about A NEW TIME-FREQUENCY APPROACH FOR UNDERDETERMINED CONVOLUTIVE BLIND SPEECH SEPARATION
- Log in to post comments
we present a new Time-Frequency approach
for recovering sources’ contribution to two convolutive
mixtures. The separation task is performed on two steps:
Each mixture is clustered into Voiced/Unvoiced frames, and
then the predominant source in each time frequency bin is
identified through a specific weight function which is based
on sources’ excitation characteristics extraction. We investigate
the performance of the proposed approach in the underdetermined
context using objective quality measures.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about A Risk-Unbiased Approach to a New Cramer-Rao Bound
- Log in to post comments
How accurately can one estimate a deterministic parameter subject to other unknown deterministic model parameters? The most popular answer to this question is given by the Cramer-Rao bound (CRB). The main assumption behind the derivation of the CRB is local unbiased estimation of all model parameters. The foundations of this work rely on doubting this assumption. Each parameter in its turn is treated as a single parameter of interest, while the other model parameters are treated as nuisance, as their mis-knowledge interferes with the estimation of the parameter of interest.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views