
DCC 2022 Conference - The Data Compression Conference (DCC) is an international forum for current work on data compression and related applications. Both theoretical and experimental work are of interest. Visit the DCC 2022 website.

- Read more about Compressing Multisets with Large Alphabets
- Log in to post comments
Current methods which compress multisets at an optimal rate have computational complexity that scales linearly with alphabet size, making them too slow to be practical in many real-world settings. We show how to convert a compression algorithm for sequences into one for multisets, in exchange for an additional complexity term that is quasi-linear in sequence length. This allows us to compress multisets of independent and identically distributed symbols at an optimal rate, with computational complexity decoupled from the alphabet size.
- Categories:
 207 Views
207 Views
- Read more about Adaptive bilateral matching for decoder side motion vector refinement in video coding
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents an adaptive bilateral matching technique for decoder-side motion vector refinement in video coding. It allows encoder to choose not only the conventional bilateral matching mode with symmetric motion vector difference but also the asymmetric alternatives. To study the efficiency of the proposed technique, the proposed method is integrated in the Versatile Video Coding Test Model 11.0. The experimental result reports an overall of -2.78% luma Bjøntegaard Delta rate for the random-access configurations.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views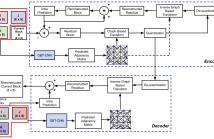
- Read more about Graph-based Transform based on 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Intra-Prediction of Imaging Data
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a novel class of Graph-based Transform based on 3D convolutional neural networks (GBT-CNN) within the context of block-based predictive transform coding of imaging data. The proposed GBT-CNN uses a 3D convolutional neural network (3D-CNN) to predict the graph information needed to compute the transform and its inverse, thus reducing the signalling cost to reconstruct the data after transformation.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about Computing Matching Statistics on Repetitive Texts
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 89 Views
89 Views
- Read more about Neural Distributed Image Compression Using Common Information
- Log in to post comments
We present a novel deep neural network (DNN) architecture for compressing an image when a correlated image is available as side information only at the decoder. This problem is known as distributed source coding (DSC) in information theory. In particular, we consider a pair of stereo images, which generally have high correlation with each other due to overlapping fields of view, and assume that one image of the pair is to be compressed and transmitted, while the other image is available only at the decoder.
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views
- Read more about Joint Rate Distortion Optimization with CNN-based In-Loop Filter For Hybrid Video Coding
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views
- Read more about Stochastic Model of Block Segmentation Based on Improper Quadtree and Optimal Code under the Bayes Criterion
- Log in to post comments
Most previous studies on lossless image compression have focused on improving preprocessing functions to reduce the redundancy of pixel values in real images. However, we assumed stochastic generative models directly on pixel values and focused on achieving the theoretical limit of the assumed models. In this study, we proposed a stochastic model based on improper quadtrees. We theoretically derive the optimal code for the proposed model under the Bayes criterion. In general, Bayes-optimal codes require an exponential order of calculation with respect to the data lengths.
- Categories:
 77 Views
77 Views
- Read more about Deep Correlated Image Set Compression Based on Distributed Source Coding and Multi-Scale Fusion
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a deep correlated image set compression scheme based on Distributed Source Coding(DSC) and multi-scale image fusion. As there exists strong correlation among images in a similar image set, we propose to utilize such correlation to generate side information at decoder side for each image in the set. Specifically, a reference structure of the image set is generated by building a minimum spanning tree according to the similarity between two images at encoder.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views- Read more about Graphs can be succinctly indexed for pattern matching in O(E^2 + V^{2.5}) time
- Log in to post comments
For the first time we provide a \emph{succinct} pattern matching index for \emph{arbitrary} graphs that can be built \emph{in polynomial time}, while improving both space and query time bounds from [SODA 2021].
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views- Read more about Linear-time minimization of Wheeler DFAs
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
Wheeler DFAs (WDFAs) are a sub-class of finite-state automata which is playing an important role in the emerging field of \emph{compressed data structures}: as opposed to general automata, WDFAs can be stored in just $\log\sigma + O(1)$ bits per edge, $\sigma$ being the alphabet's size, and support optimal-time pattern matching queries on the substring closure of the language they recognize. An important step to achieve further compression is minimization.
- Categories:
 136 Views
136 Views