
The fifth IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP) will be held in Montreal, Quebec, Canada on November 14-16, 2017. GlobalSIP is a flagship IEEE Signal Processing Society conference. It focuses on signal and information processing with an emphasis on up-and-coming signal processing themes. The conference features world-class plenary speeches, distinguished Symposium talks, tutorials, exhibits, oral and poster sessions, and panels. Visit website.
- Read more about Efficient Segmentation-Aided Text Detection for Intelligent Robots_Poster
- Log in to post comments
Scene text detection is a critical prerequisite for many fascinating applications for vision-based intelligent robots. Existing methods detect texts either using the local information only or casting it as a semantic segmentation problem. They tend to produce a large number of false alarms or cannot separate individual words accurately. In this work, we present an elegant segmentation-aided text detection solution that predicts the word-level bounding boxes using an end-to-end trainable deep convolutional neural network.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about OBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT OF ENVELOPE ENHANCEMENT ALGORITHMS FOR ASSISTIVE HEARING DEVICES
- Log in to post comments
Individuals with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) or auditory processing disorders (APDs) often suffer from temporal processing deficits leading to degraded speech perception. The situation becomes worse in the presence of background noise. Evidence exists that the exaggeration of speech envelope may enhance intelligibility, although a comprehensive evaluation of envelope enhancement algorithms is lacking.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Influence of Audio Bandwidth Reduction on Speech Emotion Recognition by Human Subjects
- Log in to post comments
Audio bandwidth reduction is the very first processing step in any speech and audio coder. Its negative influence on perceived speech quality and intelligibility has been thoroughly studied and is therefore very well documented. This paper examines whether it also has an influence on speech emotion recognition by human subjects. Several standard telephony bandwidths, from fullband down to narrowband, are considered. Listening test results show that recognition accuracy decreases with audio bandwidth.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views- Read more about DESIGN OF BINARY LDPC CODES FOR SLEPIAN-WOLF CODING OF CORRELATED INFORMATION SOURCES
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a scheme for distributed source coding, using low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes to compress close to the Slepian-Wolf limit for correlated binary sources. First, we develop a conventional Belief Propagation (BP) algorithm LDPC decoder which takes the syndrome information into account. Subsequently, modelling the correlation between the sources as a binary symmetric channel (BSC), we replace the received probabilities in the conventional channel with the cross over probability.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about Convergence Analysis of Belief Propagation for Pairwise Linear Gaussian Models
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about FAST NEAR INFRARED FUSION-BASED ADAPTIVE ENHANCEMENT OF VISIBLE
- Log in to post comments
Visible (VS) and near infra-red (NIR) band sensors provide digital
images that capture complementary spectral radiations from a
scene. Since NIR radiations propagate well through haze, mist, or
fog, the captured NIR image contains better scene details compared
to the VS image in such cases. However, NIR radiations are material
dependent and provide little information about color or texture of
the scene’s objects. To exploit the complementary details provided
by VS and NIR images, we propose a fusion approach that adaptively
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views- Read more about FAST NEAR INFRARED FUSION-BASED ADAPTIVE ENHANCEMENT OF VISIBLE
- Log in to post comments
Visible (VS) and near infra-red (NIR) band sensors provide digital
images that capture complementary spectral radiations from a
scene. Since NIR radiations propagate well through haze, mist, or
fog, the captured NIR image contains better scene details compared
to the VS image in such cases. However, NIR radiations are material
dependent and provide little information about color or texture of
the scene’s objects. To exploit the complementary details provided
by VS and NIR images, we propose a fusion approach that adaptively
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views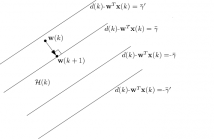
- Read more about DATA CENSORING WITH SET-MEMBERSHIP ALGORITHMS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we use the set-membership normalized least-mean-square (SM-NLMS) algorithm to censor the data set in big data applications. First, we use the distribution of the noise signal and the excess of the steady-state mean-square error (EMSE) to estimate the threshold for the desired update rate in the single threshold SM-NLMS (ST-SM-NLMS) algorithm. Then, we introduce the double threshold SM-NLMS (DT-SM-NLMS) algorithm which defines an acceptable
range of the error signal. This algorithm censors the data with very low and very high output estimation error.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views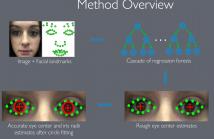
- Read more about Hybrid eye center localization using cascaded regression and robust circle fitting
- Log in to post comments
We propose a new cascaded regressor for eye center detection. Previous methods start from a face or an eye detector and use either advanced features or powerful regressors for eye center localization, but not both. Instead, we detect the eyes more accurately using an existing facial feature alignment method. We improve the robustness of localization by using both advanced features and powerful regression machinery. Finally, unlike most other methods that do not refine the regression results, we make the localization more accurate by adding a robust circle fitting post-processing step.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Heart Sound Segmentation using Switching Linear Dynamical Models
- Log in to post comments
Localization of exact positions of the fundamental heart sounds (FHS) is an essential step towards automatic analysis of heart sound phonocardiogram (PCG) recordings, the automatic segmentation allows for data-driven classification of heart pathological events. Current approach using probabilistic models such as hidden Markov models (HMMs) has improved accuracy of heart sound segmentation.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views