
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about RECONSTRUCTION OF POLARIZATION IMAGES FROM A MULTIMOD LIGHT FIELD CAMERA BASED ON THE ALIASING MODEL
- Log in to post comments
ICIP-1721.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views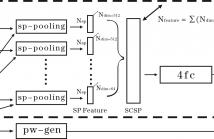
- Read more about SINGLE IMAGE DEPTH PREDICTION USING SUPER-COLUMN SUPER-PIXEL FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
Depth prediction from a single monocular image is a challenging yet valuable task, as often a depth sensor is not available. The state-of-the-art approach \cite{Liu2016} combines a deep fully convolutional network (DFCN) with a conditional random field (CRF), allowing the CRF to correct and smooth the depth values estimated by the DFCN according to efficient contextual modeling.
poster-surf.pdf
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Read more about EXPLOITING PROBABILISTIC RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN ACTION CONCEPTS FOR COMPLEX EVENT CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Videos of complex events are difficult to represent solely as
bags of low level features. Increasingly, supervised concepts
or attributes are being employed as the intermediate representation
of such videos. We propose a probabilistic framework
that models the conditional relationships between the
concepts and events and devise an approximate yet tractable
solution to infer the posterior distribution to perform event
classification. Using noisy outputs of pre-trained concept detectors,
we learn semantic and visual dependencies between
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about LEARNING CIRCULANT SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES FOR FAST IMAGE SEARCH
- Log in to post comments
Binary hashing is an established approach for fast, approximate image search. It maps a query image to a binary vector so that Hamming distances approximate image similarities. Applying the hash function can be made fast by using a circulant matrix and the fast Fourier transform, but this circulant hash function must be learned optimally from training data. We show that a previously proposed learning algorithm based on optimization in the frequency domain is suboptimal.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about POLSAR DATA ONLINE CLASSIFICATION BASED ON MULTI-VIEW LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) plays an indispensable part in remote sensing. With its development and application, rapid and accurate online classification for PolSAR data becomes more and more important. PolSAR data can be depicted by different features such as polarimetric, texture and color features, which can be considered as multiple views. In this paper, we propose an online multiview
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about TRAINING SAMPLE SELECTION FOR DEEP LEARNING OF DISTRIBUTED DATA
- Log in to post comments
The success of deep learning—in the form of multi-layer neural networks — depends critically on the volume and variety of training data. Its potential is greatly compromised when training data originate in a geographically distributed manner and are subject to bandwidth constraints. This paper presents a data sampling approach to deep learning, by carefully discriminating locally available training samples based on their relative importance.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views- Read more about ATTRIBUTE-CONTROLLED FACE PHOTO SYNTHESIS FROM SIMPLE LINE DRAWING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about TOWARDS THINNER CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS THROUGH GRADUALLY GLOBAL PRUNING
- Log in to post comments
Deep network pruning is an effective method to reduce the storage and computation cost of deep neural networks when applying them to resource-limited devices. Among many pruning granularities, neuron level pruning will remove redundant neurons and filters in the model and result in thinner networks. In this paper, we propose a gradually global pruning scheme for neuron level pruning. In each pruning step,
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views