- Bioimaging and microscopy
- Bioinformatics
- Biomedical signal processing
- Medical image analysis
- Medical imaging

- Read more about Fast dictionary-based approach for mass spectrometry data analysis
- Log in to post comments
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a fundamental technology of analytical chemistry for measuring the structure of molecules, with many application fields such as clinical biomarker analysis or pharmacokinetics. In the context of proteomic analysis with MS, the superposition of the isotopic patterns of different proteins, in various charge-states produces MS spectra difficult to decipher. The complexity of the pattern models and the large size of the data again increase the difficulty of the analysis step.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views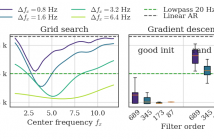
In non-linear autoregressive models, the time dependency of coefficients is often driven by a particular time-series which is not given and thus has to be estimated from the data. To allow model evaluation on a validation set, we describe a parametric approach for such driver estimation. After estimating the driver as a weighted sum of potential drivers, we use it in a non-linear autoregressive model with a polynomial parametrization. Using gradient descent, we optimize the linear filter extracting the driver, outperforming a typical grid-search on predefined filters.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about DEEP TRANSFER LEARNING FOR EEG-BASED BRAIN COMPUTER INTERFACE
- Log in to post comments
The electroencephalography classifier is the most important component of brain-computer interface based systems. There are two major problems hindering the improvement of it. First, traditional methods do not fully exploit multimodal information. Second, large-scale annotated EEG datasets are almost impossible to acquire because biological data acquisition is challenging and quality annotation is costly. Herein, we propose a novel deep transfer learning approach to solve these two problems.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views- Read more about Deriving 3D Shape Properties by Using Backward Wavelet Remesher
- Log in to post comments
It is important to determine 3D shape properties of a population of 3D mesh models in biomedical imaging issues. In contrast to conventional 3D shape analysis techniques focusing on applications like shape matching and shape retrieval, we propose in this paper a strategy capable to collect statistical information of multiple triangular mesh models. Our method operates in a coarse-to-fine fashion based on wavelet synthesis. Hence, its analysis result can be invariant against the triangular tiling of the input mesh model.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about 3D SHAPE ASYMMETRY ANALYSIS USING CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN PARTIAL GEODESIC CURVES
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Analyzing the asymmetry of anatomical shapes is one of the cornerstones of efficient computerized diagnosis. In the application of scoliotic trunk analysis, one major challenge is the high variability and complexity of deformations due to the pathology itself, and to changes of body poses, for instance, torsos acquired in lateral bending poses for surgical planning. In this paper, we present a novel and fully automatic approach to analyzing the asymmetry of deformable trunk shapes.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about CIRCLET BASED FRAMEWORK FOR OPTIC DISK DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Optic Disc (OD) detection in retinal fundus images is a crucial stage for the automation of a screening system in diabetic ophthalmology. Most researches for automatic localization of OD benefit the regions of vessels. In this paper, we present a fast and novel method based on the Circlet Trans-form to detect OD in digital retinal fundus images that doesn’t utilize the location of the vessels. First, each R, G and B band is enhanced using CLAHE method. Then, the enhanced image in RGB color space is converted to L*a*b one.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about ALIGNMENT OF OPTIC NERVE HEAD OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY B-SCANS IN RIGHT AND LEFT EYES
- Log in to post comments
Symmetry analysis of right and left eyes can be a useful tool for early detection of eye diseases. In this study, we want to compare the Optical Coherent Tomography (OCT) images captured from optic nerve head (ONH) of right and left eyes. To do this, it is necessary to align the OCT data and com-pare equivalent B-scans in right and left eyes.
icip_7.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about A KNOWLEDGE-DRIVEN FRAMEWORK FOR ECG REPRESENTATION AND INTERPRETATION FOR WEARABLE APPLICATIONS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 ViewsWith developments in experimental connectomics producing wiring diagrams of many neuronal networks, there is emerging interest in theories to understand the relationship between structure and function. Efficiency of information flow in networks has been proposed as a key functional in characterizing cognition, and we have previously shown that information-theoretic limits on information flow are predictive of behavioral speed in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.
Varshney.pdf
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views