- Bioimaging and microscopy
- Bioinformatics
- Biomedical signal processing
- Medical image analysis
- Medical imaging

- Read more about UNCERTAINTY-GUIDED PERSON SEARCH MODEL WITH AUXILIARY SHALLOW FEATURE EXPLORATION
- Log in to post comments
Person search is a unified system aimed at jointly localizing and identifying a person of interest from a gallery of whole scene images. Due to the inherent properties of the person search, it faces significant challenges of large-scale variations, inaccurate detection boxes, and crowded scenes. To address these issues, we proposed an uncertainty-guided framework coupled with auxiliary shallow feature exploration, which includes a shallow feature fusion module and an uncertaintyguided module.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about Supplementary materials for "Uncovering communities of pipelines in the task-fMRI analytical space""
- Log in to post comments
Analytical workflows in functional magnetic resonance imaging are highly flexible with limited best practices as to how to choose a pipeline. While it has been shown that the use of different pipelines might lead to different results, there is still a lack of understanding of the factors that drive these differences and of the stability of these differences across contexts. We use community detection algorithms to explore the pipeline space and assess the stability of pipeline relationships across different contexts.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views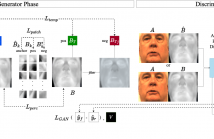
- Read more about WHEN VISIBLE-TO-THERMAL FACIAL GAN BEATS CONDITIONAL DIFFUSION
- Log in to post comments
Thermal facial imagery offers valuable insight into physiological states such as inflammation and stress by detecting emitted radiation in the infrared spectrum, which is unseen in the visible spectra. Telemedicine applications could benefit from thermal imagery, but conventional computers are reliant on RGB cameras and lack thermal sensors. As a result, we propose the Visible-to-Thermal Facial GAN (VTF-GAN) that is specifically designed to generate high-resolution thermal faces by learning both the spatial and frequency domains of facial regions, across spectra.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about MULTIMODAL EMOTION RECOGNITION WITH SURGICAL AND FABRIC MASKS
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we investigate how different types of masks affect automatic emotion classification in different channels of audio, visual, and multimodal. We train emotion classification models for each modality with the original data without mask and the re-generated data with mask respectively, and investigate how muffled speech and occluded facial expressions change the prediction of emotions.
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views
- Read more about MULTI-DOMAIN UNPAIRED ULTRASOUND IMAGE ARTIFACT REMOVAL USING A SINGLE CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
Ultrasound imaging (US) often suffers from distinct image artifacts from various sources. Classic approaches for solving these problems are usually model-based iterative approaches that have been developed specifically for each type of artifact, which are often computationally intensive. Recently, deep learning approaches have been proposed as computationally efficient and high performance alternatives. Unfortunately, in the current deep learning approaches, a dedicated neural network should be trained with matched training data for each artifact type.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Nuclear Density Distribution Feature Improved The Cervical histopathological Image Classification
- Log in to post comments
icip (6).pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about SEGMENTATION OF RETINAL ARTERIAL BIFURCATIONS IN 2D ADAPTIVE OPTICS OPHTHALMOSCOPY IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
The study of vascular morphometry requires segmenting vessels with high precision. Of particular clinical interest is the morphometric analysis of arterial bifurcations in Adaptive Optics Ophthalmoscopy (AOO) images of eye fundus. In this paper, we extend our previous approach for segmenting retinal vessel branches to the segmentation of bifurcations. This enables us to recover the microvascular tree and extract biomarkers that charactarize the blood flow.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views- Read more about Adaptive Subspace Detector in High Dimensional Space with Insufficient Training Data
- Log in to post comments
Adaptive subspace detectors (ASD) generalize matched subspace detectors (MSD) by accounting for possible correlation. Both ASD and MSD are derived using the generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT). While MSD assumes there is no correlation between observations, ASD estimates a sample covariance matrix of possibly correlated samples using signal-free observations. In this paper, we address the performance of the ASD when the number of secondary data is insufficient and the observed signal lies in higher dimensional space.
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views