- Bioimaging and microscopy
- Bioinformatics
- Biomedical signal processing
- Medical image analysis
- Medical imaging
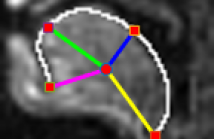
- Read more about EXTRACTION OF TONGUE CONTOUR IN REAL-TIME MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SEQUENCES
- Log in to post comments
Real-time magnetic resonance imaging (rtMRI) is becoming a practical tool in speech production research and language pathology observation. It is still a challenge to extract the tongue contour accurately in rtMRI sequences, since tongue is a soft tissue and often touches other organs such as lips and upper mandible. This paper proposes a novel semi-automatic tongue contour extraction method from rtMRI sequences. The initial boundary image is obtained by combined multi-directional Sobel operators in tongue movement region; then a boundary intensity map is constructed to find the most probable tongue contour points by searching for the optimal boundary route with Viterbi algorithm; finally the tongue contour is obtained using B-Spline approximation. The proposed method could obtain accurate tongue contour from rtMRI sequences, even in the cases that some parts of tongue touch other organs. Experiments demonstrate the robustness of the proposed method.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about Sparse Signal Recovery Methods for Variant Detection in Next-Generation Sequencing Data
- Log in to post comments
Abstract:
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Quantifying Cooperation in Choir Singing: Respiratory and Cardiac Synchronisation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Blind polychromatic X-Ray CT reconstruction from Poisson measurements
- Log in to post comments
X-ray sources are polychromatic. Ignoring this fact when performing reconstruction leads to artifacts, such as cupping and streaking, in reconstructed images. We first propose a new model parameterization that allows for blind correction of these artifacts and then develop reconstruction algorithms based on this parameterization.
Here, blind correction means that we do not know
- incident spectrum (which is an X-ray machine characteristic) and
- mass attenuation (inspected material).
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about PCA BASED ALGORITHM FOR LONGITUDINAL BRAIN TUMOR STAGE CLASSIFICATION AND DYNAMICALMODELING OF TUMOR DECAY IN RESPONSE TO VB-111 VIROTHERAPY
- Log in to post comments
In this dissertation, we propose the first, to the best of our knowledge, PCA based algorithm to noninvasively recognize and classify different temporal stages of brain tumors given a large time series of MRI images. We propose an algorithm that addresses the challenging task of classifying stage of tumor over period of time while the tumor is being treated with VB-111 virotherapy. Our approach treats stage tumor recognition as a two-dimensional recognition problem. Detecting the stage of the tumor is a crucial prognosis factor for predicting the progression of cancer and patient survival.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views- Read more about A Time-Frequency Based Bivariate Synchrony Measure for Reducing Volume Conduction Effects in EEG
- Log in to post comments
Phase synchrony measures computed on electrophysiological signals play an important role in the assessment of cognitive and sensory processes. However, due to the effects of volume conduction false synchronization values may arise between time series. Measures such as the imaginary part of coherence (ImC), phase-lag index (PLI) and an enhanced version of it, the weighted PLI (WPLI) have been proposed in order to attenuate the effects of volume conduction.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about Brain Functional Connectivity Analysis Using Mutual Information
- Log in to post comments
presentation.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about IMAGE UNMIXING SUCCESS ESTIMATION IN SPATIALLY VARYING SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views