
In this paper, we propose a novel thermal face recognition based on physiological information. The training phase includes preprocessing, feature extraction and classification. In the beginning, the human face can be depicted from the background of thermal image using the Bayesian framework and normalized to uniform size. A grid of 22 thermal points is extracted as a feature vector. These 22 extracted points are used to train Linear Support Vector Machine Classifier (linear SVC). The classifier calculates the support vectors and uses them to find the hyperplane for classification.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Effective and Stable Neuron Model Optimization Based on Aggregated CMA-ES
- Log in to post comments
Computer simulations have facilitated our understanding of the dynamic behavior of the brain and the effect of the medical treatment such as deep brain stimulation. For improving the simulation model, it is essential to develop a method for optimizing parameters of a neuron model from available experimental data. In this paper, we apply Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolutionary Strategy (CMA-ES) to the parameter optimization problem, and compare it with widely used conventional approaches including genetic algorithm (GA) and the Nelder-Mead method.
poster v10.pdf
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
- Read more about eep Latent Factor Model for Predicting Drug Target Interactions
- Log in to post comments
In drug target interaction (DTI) the interactions of some (a subset) drugs on some (a subset) targets are known. The goal is to predict the interactions of all drugs on all targets. One approach is to formulate this as a matrix completion problem, where the matrix of interactions having drugs along the rows and targets along the columns is partially filled. So far standard matrix completion approaches such as nuclear norm minimization and matrix factorization have been used to address the problem.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views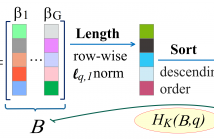
- Read more about Compressive Regularized Discriminant Analysis of High-Dimensional Data with Applications to Microarray Studies
- Log in to post comments
We propose a modification of linear discriminant analysis, referred to as compressive regularized discriminant analysis (CRDA), for analysis of high-dimensional datasets. CRDA is specially designed for feature elimination purpose and can be used as gene selection method in microarray studies. CRDA lends ideas from ℓq,1 norm minimization algorithms in the multiple measurement vectors (MMV) model and utilizes joint-sparsity promoting hard thresholding for feature elimination.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views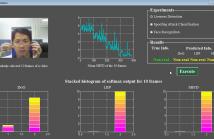
- Read more about Face Liveness Detection Using Shearlet Based Feature Descriptors
- Log in to post comments
We demonstrate the results of DoG and LBP for comparison purpose. This demo video is available at this link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kUCC0hLSJaU. In addition, in order to show that the proposed method can be directly used in real situation, we completed a real-time implementation of our method and tested it using real data which also include print photo attack, mobile photo attack and video attack. In this demo, 21 frames are analyzed for each detection and the final result is the average score of these 21 frames.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views- Read more about FACE LIVENESS DETECTION AND RECOGNITION USING SHEARLET BASED FEATURE DESCRIPTORS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
Ph.D. Thesis by Donald McCuan (advisor Andrew Knyazev), Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Colorado Denver, 2012, originally posted at http://math.ucdenver.edu/theses/McCuan_PhdThesis.pdf (1157)
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about Novel data clustering for microarrays and image segmentation
- Log in to post comments
We develop novel algorithms and software on parallel computers for data clustering of large datasets. We are interested in applying our approach, e.g., for analysis of large datasets of microarrays or tiling arrays in molecular biology and for segmentation of high resolution images.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Multiresolution Functional Connectivity Analysis Refines Functional Connectivity Networks in Individual Brains
- Log in to post comments
Recent advances in functional connectivity (FC) analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data facilitate the characterization of the brain’s intrinsic functional networks (FC-fMRI). Because the fMRI signal does not provides a perfect representation of neuronal activity, the potential for FC-fMRI to identify functionally relevant networks critically depends upon separating overlapping signals from one another and from external noise. As a step in data preconditioning, researchers often band-pass filter fMRI signals to the range from 0.01 Hz to 0.1 Hz.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about A Riemannian Approach for Computing Geodesic in Elastic Shape Analysis
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views