
Event cameras, which detect local brightness changes instead of capturing full-frame images, offer high temporal resolution and low latency. Although existing convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformer-based methods for event-based video reconstruction have achieved impressive results, they suffer from high computational costs due to their linear operations. These methods often require 10M-30M parameters and inference times of 30-110 ms per forward pass at a resolution of 640\times480 on modern GPUs.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Materials For ICIP2025
- Log in to post comments
Supplementary Materials of "CURVE: CLIP-Utilized Reinforcement learning for Visual image Enhancement via Simple Image Processing" submitted to ICIP 2025
- Categories:
 195 Views
195 Views
- Read more about Supplementary material for "Geometry Regularized Point Cloud Autoencoder"
- Log in to post comments
Point cloud is a prevalent format in representing 3D geometry. Regardless of the recent advances, unsupervised learning for 3D point clouds remains arduous for various tasks due to its unorganized and sparsely distributed nature. To address this challenge, we propose a geometry regularized point cloud autoencoder, aiming to preserve local geometry structure. In particular, based on the Mahalanobis distance, we propose a point cloud geometry metric counting the local statistics. It endeavors to maximize the posterior of the reconstruction conditioned on the input point cloud.
GRAE_supp.pdf
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Material for Test-time Vocabulary Adaptation for Language-driven Object Detection
- Log in to post comments
This document is the supplementary material for the paper submission: Test-time Vocabulary Adaptation for Language-driven Object Detection.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Material for Test-time Vocabulary Adaptation for Language-driven Object Detection
- Log in to post comments
This is the supplementary material for the paper submission: Test-time Vocabulary Adaptation for Language-driven Object Detection.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Supplementary Material for Test-time Vocabulary Adaptation for Language-driven Object Detection
- Log in to post comments
This document serves as the supplementary material for the paper submission Test-time Vocabulary Adaptation for Language-driven Object Detection.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for GGMix
- Log in to post comments
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for GGMix
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about ENACT: Entropy-based Clustering of Attention Input for Reducing the Computational Resources of Object Detection Transformers - Supplementary Material
- Log in to post comments
Transformers demonstrate competitive performance in terms of precision on the problem of vision-based object detection. However, they require considerable computational resources due to the quadratic size of the attention weights.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views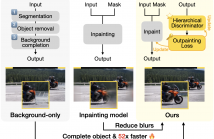
- Read more about In2Out: Fine-Tuning Video Inpainting Model for Video Outpainting using Hierarchical Discriminator
- Log in to post comments
Video outpainting presents a unique challenge of extending the borders while maintaining consistency with the given content. In this paper, we suggest the use of video inpainting models that excel in object flow learning and reconstruction in outpainting rather than solely generating the background as in existing methods. However, directly applying or fine-tuning inpainting models to outpainting has shown to be ineffective, often leading to blurry results.
- Categories:
 209 Views
209 Views
- Read more about Supplementary FMG-Det: Foundation Model Guided Robust Object Detection
- Log in to post comments
Collecting high quality data for object detection tasks is challenging due to the inherent subjectivity in labeling the boundaries of an object. This makes it difficult to not only collect consistent annotations across a dataset but also to validate them, as no two annotators are likely to label the same object using the exact same coordinates. These challenges are further compounded when object boundaries are partially visible or blurred, which can be the case in many domains.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views