
- Read more about CHANNEL-SPATIAL TRANSFORMER FOR EFFICIENT IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION
- Log in to post comments
Transformer has achieved remarkable success in low-level visual tasks, including image super-resolution (SR), owing to its ability to establish global dependencies through self-attention mechanism. However, existing methods overlook the mutual influence and promotion between the channel and spatial dimensions. The feed-forward network (FFN) in the transformer architecture introduces redundant information in the channel during feature extraction, hindering feature representation capability and neglecting spatial information modeling.
poster_1446.pdf
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Camera Calibration Using a Single View of a Symmetric Object
- Log in to post comments
This paper addresses the problem of camera calibration and shape recovery using a single image of a reflectively symmetric object. Unlike existing methods requiring knowledge of 3D points or two images, this paper proposes to calibrate camera parameters using one image with known point distance ratios on 3D object. Specifically, we first recover the vanishing point of the symmetry plane normal. Then a set of candidate focal lengths are uniformly selected as the initial values, from which the pan and yaw angles of the camera can be obtained.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about CENET: CONTENT-AWARE ENHANCED NETWORK FOR PRACTICAL SCENE PARSING
- Log in to post comments
Attention mechanisms are widely adopted in existing scene parsing methods due to their excellent performance, especially spatial self-attention. However, spatial self-attention suffers from high computational complexity, which limits the practical applications of the scene parsing methods on mobile devices with limited resources. In view of this, we propose a simple yet effective spatial attention module, namely Content-Aware Attention Module (CAAM).
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
Traditional frame-based cameras inevitably suffer from non-uniform blur in real-world scenarios. Event cameras that record the intensity changes with high temporal resolution provide an effective solution for image deblurring. In this paper, we formulate the event-based image deblurring as an image generation problem by designing diffusion priors for the image and residual. Specifically, we propose an alternative diffusion sampling framework to jointly estimate clear and residual images to ensure the quality of the final result.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views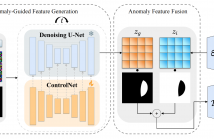
- Read more about Slides for CAGEN
- Log in to post comments
Data augmentation has been widely applied in anomaly detection, which generates synthetic anomalous data for training. However, most existing anomaly augmentation methods focus on image-level cut-and-paste techniques, resulting in less realistic synthetic results, and are restricted to a few predefined patterns. In this paper, we propose our Controllable Anomaly Generator (CAGen) for anomaly data augmentation, which can generate high-quality images, and be flexibly controlled with text prompts.
ICASSP.pptx
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views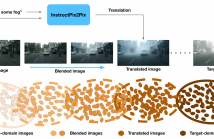
- Read more about BLENDA: DOMAIN ADAPTIVE OBJECT DETECTION THROUGH DIFFUSION-BASED BLENDING
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) aims to transfer a model learned using labeled data from the source domain to unlabeled data in the target domain. To address the large domain gap issue between the source and target domains, we propose a novel regularization method for domain adaptive object detection, BlenDA, by generating the pseudo samples of the intermediate domains and their corresponding soft domain labels for adaptation training.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about X-CAUNET: CROSS-COLOR CHANNEL ATTENTION WITH UNDERWATER IMAGE-ENHANCING TRANSFORMER
- Log in to post comments
Underwater image enhancement is essential to mitigate the environment-centric noise in images, such as haziness, color degradation, etc. With most existing works focused on processing an RGB image as a whole, the explicit context that can be mined from each color channel separately goes unaccounted for, ignoring the effects produced by the wavelength of light in underwater conditions. In this work, we propose a framework called X-CAUNET that addresses this
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about Benchmarking Adversarial Robustness of Image Shadow Removal with Shadow-adaptive Attacks
- Log in to post comments
Shadow removal is a task aimed at erasing regional shadows present in images and reinstating visually pleasing natural scenes with consistent illumination. While recent deep learning techniques have demonstrated impressive performance in image shadow removal, their robustness against adversarial attacks remains largely unexplored. Furthermore, many existing attack frameworks typically allocate a uniform budget for perturbations across the entire input image, which may not be suitable for attacking shadow images.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views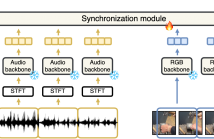
- Read more about Poster: Synchformer: Efficient Synchronization from Sparse Cues
- Log in to post comments
Our objective is audio-visual synchronization with a focus on ‘in-the-wild’ videos, such as those on YouTube, where synchronization cues can be sparse. Our contributions include a novel audio-visual synchronization model, and training that decouples feature extraction from synchronization modelling through multi-modal segment-level contrastive pre-training. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both dense and sparse settings.
vi_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about LANGUAGE-FREE COMPOSITIONAL ACTION GENERATION VIA DECOUPLING REFINEMENT
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Composing simple actions into complex actions is crucial yet challenging. Existing methods largely rely on language annotations to discern composable latent semantics, which is costly and labor-intensive. In this study, we introduce a novel framework to generate compositional actions without language auxiliaries. Our approach consists of three components: Action Coupling, Conditional Action Generation, and Decoupling Refinement. Action Coupling integrates two subactions to generate pseudo-training examples.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views