
- Read more about ICIP2025_Supplementary_ESCANet
- Log in to post comments
While deep learning based solutions, including CNNs or transformer-based architectures, have demonstrated promising results for image super-resolution (SR) tasks, their substantial depth and parameters challenge deployment on edge computing AI-enabled devices. To address this issue, we propose a lightweight single image super-resolution (SISR) model named Efficient Spatial and Channel Attentive Network (ESCANet), comprised of Spatial Enhancement Module (SEM) and Channel-wise Enhancement Module (CEM).
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
Previous works on image inpainting mainly focus on inpainting background or partially missing objects, while the problem of inpainting an entire missing object remains unexplored.
This work studies a new image inpainting problem,~\ie shape-guided object inpainting. Given an incomplete input image, the goal is to fill in the hole by generating an object based on the context and the implicit guidance provided by the hole shape.
We propose a new data preparation method and a novel Contextual Object Generator for the object inpainting task.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about ICIP2025_3D_360ExtremelySparseViews
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Novel view synthesis in 360$^\circ$ scenes from extremely sparse input views is essential for applications like virtual reality and augmented reality. This paper presents a novel framework for novel view synthesis in extremely sparse-view cases. As typical structure-from-motion methods are unable to estimate camera poses in extremely sparse-view cases, we apply DUSt3R to estimate camera poses and generate a dense point cloud.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views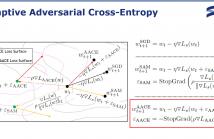
- Read more about Adaptive Adversarial Cross-Entropy Loss for Sharpness-Aware Minimization
- Log in to post comments
Recent advancements in learning algorithms have demonstrated that the sharpness of the loss surface is an effective measure for improving the generalization gap. Building upon this concept, Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) was proposed to enhance model generalization and achieved state-of-the-art performance. SAM consists of two main steps, the weight perturbation step and the weight updating step. However, the perturbation in SAM is determined by only the gradient of the training loss, or cross-entropy loss.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Rethinking temporal self-similarity for repetitive action counting
- Log in to post comments
Counting repetitive actions in long untrimmed videos is a challenging task that has many applications such as rehabilitation. State-of-the-art methods predict action counts by first generating a temporal self-similarity matrix (TSM) from the sampled frames and then feeding the matrix to a predictor network. The self-similarity matrix, however, is not an optimal input to a network since it discards too much information from the frame-wise embeddings.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Fast Unsupervised Tensor Restoration via Low-rank Deconvolution
- Log in to post comments
Low-rank Deconvolution (LRD) has appeared as a new multi-dimensional representation model that enjoys important efficiency and flexibility properties. In this work we ask ourselves if this analytical model can compete against Deep Learning (DL) frameworks like Deep Image Prior (DIP) or Blind-Spot Networks (BSN) and other classical methods in the task of signal restoration. More specifically, we propose to extend LRD with differential regularization.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about Fast Unsupervised Tensor Restoration via Low-rank Deconvolution
- Log in to post comments
Low-rank Deconvolution (LRD) has appeared as a new multi-dimensional representation model that enjoys important efficiency and flexibility properties. In this work we ask ourselves if this analytical model can compete against Deep Learning (DL) frameworks like Deep Image Prior (DIP) or Blind-Spot Networks (BSN) and other classical methods in the task of signal restoration. More specifically, we propose to extend LRD with differential regularization.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about LIGHTWEIGHT UNDERWATER IMAGE ENHANCEMENT VIA IMPULSE RESPONSE OF LOW-PASS FILTER BASED ATTENTION NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose an improved model of Shallow-UWnet for underwater image enhancement. In the proposed method, we enhance the learning process and solve the vanishing gradient problem by a skip connection, which concatenates the raw underwater image and the low-pass filter (LPF) impulse response into Shallow-UWnet. Additionally, we integrate the simple, parameter-free attention module (SimAM) into each Convolution Block to enhance the visual quality of images.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views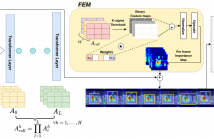
- Read more about ET: Explain to Train: Leveraging Explanations to Enhance the Training of A Multimodal Transformer
- Log in to post comments
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) has become increasingly vital for improving the transparency and reliability of neural network decisions. Transformer architectures have emerged as the state-of-the-art for various tasks across single modalities such as video, language, or signals, as well as for multimodal approaches. Although XAI methods for transformers are available, their potential impact during model training remains underexplored.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views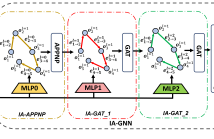
- Read more about Driving through Graphs: A Bipartite Graph for Traffic Scene Analysis
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a novel approach for traffic scene analysis in driving videos by exploring spatio-temporal relationships captured by a temporal frame-to-frame (f2f) bipartite graph, eliminating the need for complex image-level high-dimensional feature extraction. Instead, we rely on object detectors that provide bounding box information. The proposed graph approach efficiently connects objects across frames where nodes represent essential object attributes, and edges signify interactions based on simple spatial metrics such as distance and angles between objects.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views