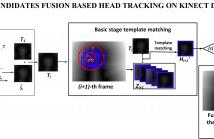
- Read more about REAL-TIME MULTI-CANDIDATES FUSION BASED HEAD TRACKING ON KINECT DEPTH SEQUENCE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about Ship wake detection for sar images with complex backgrounds based on morphological dictionary learning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Ship wake detection for sar images with complex backgrounds based on morphological dictionary learning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Bernstein Filter: a new solver for mean curvature regularized models
- Log in to post comments
The mean curvature has been shown a proper regularization in various ill-posed inverse problems in signal processing. Traditional solvers are based on either gradient descent methods or Euler Lagrange Equation. However, it is not clear if this mean curvature regularization term itself is convex or not. In this paper, we first prove that the mean curvature regularization is convex if the dimension of imaging domain is not
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Supervised-learning based face hallucination for enhancing face recognition
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a two-step supervised face hallucination framework based on class-specific dictionary learning. Since the performance of learning-based face hallucination relies on its training set, an inappropriate training set (e.g., an input face image is very different from the training set) can reduce the visual quality of reconstructed high-resolution (HR) face significantly.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
Ph.D. Thesis by Donald McCuan (advisor Andrew Knyazev), Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, University of Colorado Denver, 2012, originally posted at http://math.ucdenver.edu/theses/McCuan_PhdThesis.pdf (1161)
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about Multigrid Eigensolvers for Image Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Presentation at LANL and UC Davis, 2009. Originally posted at http://math.ucdenver.edu/~aknyazev/research/conf/
LANL09.ppt
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Novel data clustering for microarrays and image segmentation
- Log in to post comments
We develop novel algorithms and software on parallel computers for data clustering of large datasets. We are interested in applying our approach, e.g., for analysis of large datasets of microarrays or tiling arrays in molecular biology and for segmentation of high resolution images.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Approximate Message Passing in Coded Aperture Snapshot Spectral Imaging
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Joint Weighted Dictionary Learning and Classifier Training for Robust Biometric Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present an automated system for robust biometric recognition based upon sparse representation and dictionary learning. In sparse representation, extracted features from the training data are used to develop a dictionary. Training data of real world applications are likely to be exposed to geometric transformations, which is a big challenge for designing of discriminative dictionaries. Classification is achieved by representing the extracted features of the test data as a linear combination of entries in the dictionary.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views