- Read more about CAPITALIZATION NORMALIZATION FOR LANGUAGE MODELING WITH AN ACCURATE AND EFFICIENT HIERARCHICAL RNN MODEL
- Log in to post comments
Capitalization normalization (truecasing) is the task of restoring the correct case (uppercase or lowercase) of noisy text. We propose a fast, accurate and compact two-level hierarchical word-and-character-based recurrent neural network model. We use the truecaser to normalize user-generated text in a Federated Learning framework for language modeling. A case-aware language model trained on this normalized text achieves the same perplexity as a model trained on text with gold capitalization.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about LATTICEBART: LATTICE-TO-LATTICE PRE-TRAINING FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
Language models (LM) have been widely deployed in modern ASR systems. The LM is often trained by minimizing its perplexity on speech transcript. However, few studies try to discriminate a "gold" reference against inferior hypotheses. In this work, we propose a large margin language model (LMLM). LMLM is a general framework that enforces an LM to assign a higher score to the "gold" reference, and a lower one to the inferior hypothesis. The general framework is applied to three pretrained LM architectures: left-to-right LSTM, transformer encoder, and transformer decoder.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
Neural network language model (NNLM) is an essential component of industrial ASR systems. One important challenge of training an NNLM is to leverage between scaling the learning process and handling big data. Conventional approaches such as block momentum provides a blockwise model update filtering (BMUF) process and achieves almost linear speedups with no performance degradation for speech recognition.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views
- Read more about Phoneme Level Language Models for Sequence Based Low Resource ASR
- Log in to post comments
Building multilingual and crosslingual models help bring different languages together in a language universal space. It allows models to share parameters and transfer knowledge across languages, enabling faster and better adaptation to a new language. These approaches are particularly useful for low resource languages. In this paper, we propose a phoneme-level language model that can be used multilingually and for crosslingual adaptation to a target language.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about Automatic Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Using Neural Network Language Models
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about ADVERSARIAL MULTI-TASK DEEP FEATURES AND UNSUPERVISED BACK-END ADAPTATION FOR LANGUAGE RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views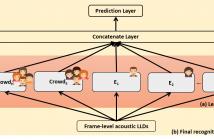
- Read more about EVERY RATING MATTERS: JOINT LEARNING OF SUBJECTIVE LABELS AND INDIVIDUAL ANNOTATORS FOR SPEECH EMOTION CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
The subjectivity and variability exist in the human emotion perception differs from person to person. In this work, we propose a framework that models the majority of emotion annotation integrated with modeling of subjectivity in improving emotion categorization performances. Our method achieves a promising accuracy of 61.48% on a four-class emotion recognition task. To the best of our knowledge, while there are many works in studying annotator subjectivity, this is one of the first works that have explicitly modeled jointly the consensus with individuality in emotion perception to demonstrate its improvement in classifying emotion in a benchmark corpus.
In our immediate future work, we will evaluate the proposed framework on other public large-scaled emotional database with multiple annotators, e.g., NNIME, to further justify its robustness. We also plan to extend our framework to includ other behavior attributes, e.g., lexical content and body movements. Furthermore, the subjective nature of emotion perception has been shown to be related to the rater personality, a joint modeling of rater’s characteristics with his/her subjectivity in emotion perception may lead to further advancement in robust emotion recognition.
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views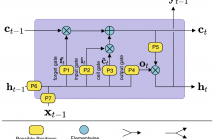
- Read more about Gaussian Process LSTM Recurrent Neural Network Language Models for Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Recurrent neural network language models (RNNLMs) have shown superior performance across a range of speech recognition tasks. At the heart of all RNNLMs, the activation functions play a vital role to control the information flows and tracking longer history contexts that are useful for predicting the following words. Long short-term memory (LSTM) units are well known for such ability and thus widely used in current RNNLMs. However, the deterministic parameter estimates in LSTM RNNLMs are prone to over-fitting and poor generalization when given limited training data.
- Categories:
 122 Views
122 Views