
Abstract—While more and more forensic techniques have been proposed to detect the processing history of multimedia content, one starts to wonder if there exists a fundamental limit on the capability of forensics. In other words, besides keeping on searching what investigators can do, it is also important to find out the limit of their capability and what they cannot do. In this work, we explore the fundamental limit of operation forensics by proposing an information theoretical framework.
double_RQ.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about Compressive Sensing Forensics
- Log in to post comments
Abstract—Identifying a signal’s origin and how it was acquired is an important forensic problem. While forensic techniques currently exist to determine a signal’s acquisition history, these techniques do not account for the possibility that a signal could be compressively sensed. This is an important problem since compressive sensing techniques have seen increased popularity in recent years. In this paper, we propose a set of forensic techniques to identify signals acquired by compressive sensing. We do this by first identifying the fingerprints left in a signal by compressive sensing.
double_AQ.pdf
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about Supplemental Material: Is Perturbation-based Image Protection Disruptive to Image Editing?
- Log in to post comments
The remarkable image generation capabilities of state-of-the-art diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion, can also be misused to spread misinformation and plagiarize copyrighted materials. To mitigate the potential risks associated with image editing, current image protection methods rely on adding imperceptible perturbations to images to obstruct diffusion-based editing. A fully successful protection for an image implies that the output of editing attempts is an undesirable, noisy image which is completely unrelated to the reference image.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about Increasing Trust in Image Analysis by Detecting Trellis Quantization in JPEG Images - ICIP'24 Slides
- Log in to post comments
JPEG image forensics investigates the authenticity and origin of compressed images. Many established methods rely on assumptions about the statistical distribution of quantized discrete cosine transform coefficients. However, JPEG implementations that use trellis quantization, such as mozjpeg, produce images that challenge these assumptions. In this study, we demonstrate that artifacts resulting from trellis quantization can compromise the reliability of established forensic methods and cause false alarms for innocuous images.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Synthesizing Black-box Anti-forensics DeepFakes with High Visual Quality
- Log in to post comments
DeepFake, an AI technology for creating facial forgeries, has garnered global attention. Amid such circumstances, forensics researchers focus on developing defensive algorithms to counter these threats. In contrast, there are techniques developed for enhancing the aggressiveness of DeepFake, e.g., through anti-forensics attacks, to disrupt forensic detectors. However, such attacks often sacrifice image visual quality for improved undetectability. To address this issue, we propose a method to generate novel adversarial sharpening masks for launching black-box anti-forensics attacks.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Slide for Interpretable Multimodal Out-of-context Detection with Soft Logic Regularization
- Log in to post comments
The rapid spread of information through mobile devices and media has led to the widespread of false or deceptive news, causing significant concerns in society. Among different types of misinformation, image repurposing, also known as out-of-context misinformation, remains highly prevalent and effective. However, current approaches for detecting out-of-context misinformation often lack interpretability and offer limited explanations. In this study, we propose a logic regularization approach for out-of-context detection called LOGRAN (LOGic Regularization for out-of-context ANalysis).
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about MDRT: MULTI-DOMAIN SYNTHETIC SPEECH LOCALIZATION
- Log in to post comments
With recent advancements in generating synthetic speech, tools to generate high-quality synthetic speech impersonating any human speaker are easily available. Several incidents report misuse of high-quality synthetic speech for spreading misinformation and for large-scale financial frauds. Many methods have been proposed for detecting synthetic speech; however, there is limited work on localizing the synthetic segments within the speech signal. In this work, our goal is to localize the synthetic speech segments in a partially synthetic speech signal.
mdrt_v05.pdf
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about LOFT: LATENT SPACE OPTIMIZATION AND GENERATOR FINE-TUNING FOR DEFENDING AGAINST DEEPFAKES
- Log in to post comments
DeepFakes pose a significant threat to individual reputations and society as a whole. Existing proactive defense strategies concentrate on adding adversarial perturbations to images to disrupt or nullify the generation of DeepFakes, but these approaches are easily detectable by human perception and can be removed. To address this challenge, we propose a three-stage framework called LOFT (Latent Space Optimization and Generator Fine-Tuning for Defending against DeepFakes). First, encoding the original image into the latent space to obtain a latent code that captures facial features.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views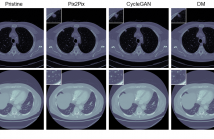
- Read more about M3DSYNTH: A DATASET OF MEDICAL 3D IMAGES WITH AI-GENERATED LOCAL MANIPULATIONS
- Log in to post comments
The ability to detect manipulated visual content is becoming increasingly important in many application fields, given the rapid advances in image synthesis methods. Of particular concern is the possibility of modifying the content of medical images, altering the resulting diagnoses. Despite its relevance, this issue has received limited attention from the research community. One reason is the lack of large and curated datasets to use for development and benchmarking purposes.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views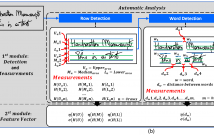
- Read more about Innovative Methods for Non-Destructive Inspection of Handwritten Documents
- Log in to post comments
Handwritten document analysis is an area of forensic science, with the goal of establishing authorship of documents through examination of inherent characteristics. Law enforcement agencies use standard protocols based on manual processing of handwritten documents. This method is time-consuming, is often subjective in its evaluation, and is not replicable.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views