- Read more about MOTION BLUR REMOVAL VIA COUPLED AUTOENCODER
- Log in to post comments
ICIP_ppt.pdf
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views- Read more about LEARNING AUTOENCODERS WITH LOW-RANK WEIGHTS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about UNDERSTANDING NEURAL-NETWORK DENOISERS THROUGH AN ACTIVATION FUNCTION PERSPECTIVE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 ViewsFully connected multi layer neural networks such as Deep Boltzmann Machines (DBM) performs better than fully connected single layer neural networks in image classification tasks and has a smaller number of hidden layer neurons than Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) based fully connected multi layer neural networks such as Multi Layer ELM (ML-ELM) and Hierarchical ELM (H-ELM) However, ML-ELM and H-ELM has a smaller training time than DBM.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views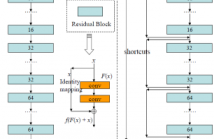
- Read more about Residual Networks of Residual Networks: Multilevel Residual Networks
- Log in to post comments
A residual-networks family with hundreds or even thousands of layers dominates major image recognition tasks, but building a network by simply stacking residual blocks inevitably limits its optimization ability. This paper proposes a novel residual-network architecture, Residual networks of Residual networks (RoR), to dig the optimization ability of residual networks. RoR substitutes optimizing residual mapping of residual mapping for optimizing original residual mapping.
ICIP 2017.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views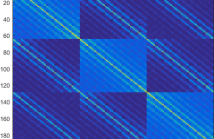
- Read more about Generating Adaptive and Robust Filter Sets using an Unsupervised Learning Framework
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we introduce an adaptive unsupervised learning framework, which utilizes natural images to train filter sets. The ap- plicability of these filter sets is demonstrated by evaluating their per- formance in two contrasting applications - image quality assessment and texture retrieval. While assessing image quality, the filters need to capture perceptual differences based on dissimilarities between a reference image and its distorted version. In texture retrieval, the filters need to assess similarity between texture images to retrieve closest matching textures.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views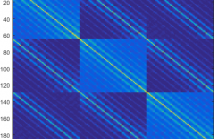
- Read more about Generating Adaptive and Robust Filter Sets using an Unsupervised Learning Framework
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we introduce an adaptive unsupervised learning framework, which utilizes natural images to train filter sets. The ap- plicability of these filter sets is demonstrated by evaluating their per- formance in two contrasting applications - image quality assessment and texture retrieval. While assessing image quality, the filters need to capture perceptual differences based on dissimilarities between a reference image and its distorted version. In texture retrieval, the filters need to assess similarity between texture images to retrieve closest matching textures.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Learning a Cross-Modal Hashing Network for Multimedia Search
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a cross-modal hashing network (CMHN) method to learn compact binary codes for cross-modality multimedia search. Unlike most existing cross-modal hashing methods which learn a single pair of projections to map each example into a binary vector, we design a deep neural network to learn multiple pairs of hierarchical non-linear transformations, under which the nonlinear characteristics of samples can be well exploited and the modality gap is well reduced.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about LEARNING TO GENERATE IMAGES WITH PERCEPTUAL SIMILARITY METRICS (SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL)
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views