
- Read more about Learning convolutional sparse coding
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
We propose a convolutional recurrent sparse auto-encoder
model. The model consists of a sparse encoder, which is a
convolutional extension of the learned ISTA (LISTA) method,
and a linear convolutional decoder. Our strategy offers a simple
method for learning a task-driven sparse convolutional
dictionary (CD), and producing an approximate convolutional
sparse code (CSC) over the learned dictionary. We trained
the model to minimize reconstruction loss via gradient decent
with back-propagation and have achieved competitve
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Document Quality Estimation using Spatial Frequency Response
- Log in to post comments
The current Document Image Quality Assessment (DIQA) algorithms directly relate the Optical Character Recognition (OCR) accuracies with the quality of the document to build supervised learning frameworks. This direct correlation has two major limitations: (a) OCR may be affected by factors independent of the quality of the capture and (b) it cannot account for blur variations within an image. An alternate possibility is to quantify the quality of capture using human judgement, however, it is subjective and prone to error.
rai_ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about AUTOMATIC MOTION ARTIFACT DETECTION FOR WHOLE-BODY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
- Log in to post comments
Magnetic resonance (MR) plays an important role in medical imaging. It can be flexibly tuned towards different applications for deriving a meaningful diagnosis. However, its long acquisition times and flexible parametrization make it on the other hand prone to artifacts which obscure the underlying image content or can be misinterpreted as anatomy. Patient-induced motion artifacts are still one of the major extrinsic factors which degrade image quality.
- Categories:
 98 Views
98 Views
- Read more about Speaker Diarization with LSTM
- Log in to post comments
For many years, i-vector based audio embedding techniques were the dominant approach for speaker verification and speaker diarization applications. However, mirroring the rise of deep learning in various domains, neural network based audio embeddings, also known as d-vectors, have consistently demonstrated superior speaker verification performance. In this paper, we build on the success of d-vector based speaker verification systems to develop a new d-vector based approach to speaker diarization.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about ATTENTION-BASED MODELS FOR TEXT-DEPENDENT SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Attention-based models have recently shown great performance on a range of tasks, such as speech recognition, machine translation, and image captioning due to their ability to summarize relevant information that expands through the entire length of an input sequence. In this paper, we analyze the usage of attention mechanisms to the problem of sequence summarization in our end-to-end text-dependent speaker recognition system. We explore different topologies and their variants of the attention layer, and compare different pooling methods on the attention weights.
- Categories:
 162 Views
162 Views
- Read more about Improving the Capacity of Very Deep Networks with Maxout Units
- Log in to post comments
Deep neural networks inherently have large representational power for approximating complex target functions. However,
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about HOW SAMPLING RATE AFFECTS CROSS-DOMAIN TRANSFER LEARNING FOR VIDEO DESCRIPTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about AI: A Signal Processing Perspective
- Log in to post comments
The signal processing (SP) landscape has been enriched by recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), especially since 2010 or so, yielding new tools for signal estimation, classification, prediction, and manipulation. Layered signal representations, nonlinear function approximation, and nonlinear signal prediction are now feasible at very large scale in both dimensionality and data size.
- Categories:
 2657 Views
2657 Views- Read more about Learning Local Receptive Fields and their Weight Sharing Scheme on Graphs
- Log in to post comments
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views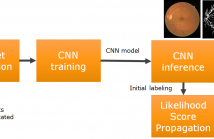
- Read more about ARTERY/VEIN CLASSIFICATION IN FUNDUS IMAGES USING CNN AND LIKELIHOOD SCORE PROPAGATION
- Log in to post comments
Artery/vein classification in fundus images is a prerequisite for the assessment of diseases such as diabetes, hypertension or other cardiovascular pathologies. One clinical measure used to assess the severity of cardiovascular risk is the retinal arterio-venous ratio (AVR), which significantly depends on the accuracy of vessel classification into arteries or veins. This paper proposes a novel method for artery/vein classification combining deep learning and graph propagation strategies.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views