
- Read more about Compact Polyominoes
- Log in to post comments
We provide a compact representation of polyominoes with n cells that supports navigation and visibility queries in constant time.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Rate-distortion Optimized Coding for Efficient CNN Compression
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a coding framework for deep convolutional neural network compression. Our approach utilizes the classical coding theories and formulates the compression of deep convolutional neural networks as a rate-distortion optimization problem. We incorporate three coding ingredients in the coding framework, including bit allocation, dead zone quantization, and Tunstall coding, to improve the rate-distortion frontier without noticeable system-level overhead introduced.
- Categories:
 180 Views
180 Views
- Read more about Compressive Sensing via Unfolded ℓ_0-Constrained Convolutional Sparse Coding
- Log in to post comments
DCC的副本.pdf
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views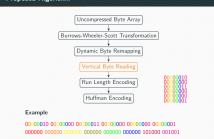
The Run Length Encoding (RLE) compression method is a long standing simple lossless compression scheme which is easy to implement and achieves a good compression on input data which contains repeating consecutive symbols. In its pure form RLE is not applicable on natural text or other input data with short sequences of identical symbols. We present a combination of preprocessing steps that turn arbitrary input data in a byte-wise encoding into a bit-string which is highly suitable for RLE compression.
- Categories:
 349 Views
349 Views
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views
- Read more about SRQ: Self-reference quantization scheme for lightweight neural network
- Log in to post comments
Lightweight neural network (LNN) nowadays plays a vital role in embedded applications with limited resources. Quantized LNN with a low bit precision is an effective solution, which further reduces the computational and memory resource requirements. However, it is still challenging to avoid the significant accuracy degradation compared with the heavy neural network due to its numerical approximation and lower redundancy. In this paper, we propose a novel robustness-aware self-reference quantization scheme for LNN (SRQ), as Fig.
dcc2021.pdf
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about Joint Asymmetric Convolution Block and LocalGlobal Context Optimization for Learned Image Compression
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about A Dual-Critic Reinforcement Learning Framework for Frame-level Bit Allocation in HEVC/H.265
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces a dual-critic reinforcement learning (RL) framework to address the problem of frame-level bit allocation in HEVC/H.265. The objective is to minimize the distortion of a group of pictures (GOP) under a rate constraint. Previous RL-based methods tackle such a constrained optimization problem by maximizing a single reward function that often combines a distortion and a rate reward. However, the way how these rewards are combined is usually ad hoc and may not generalize well to various coding conditions and video sequences.
- Categories:
 81 Views
81 Views
- Read more about Parallel Processing of Grammer Compression
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views