
- Read more about HOLISTIC SEMI-SUPERVISED APPROACHES FOR EEG REPRESENTATION LEARNING
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Feature Fusion Ensemble Architecture With Active Learning For Microscopic Blood Smear Analysis
- Log in to post comments
The blood smear analysis provides vital information and forms the basis to diagnose most of the diseases. With recent developments, deep learning methods can analyze the microscopic blood sample using image processing and classification tasks with less human effort and increased accuracy.
- Categories:
 153 Views
153 Views
In machine learning, classifiers are typically susceptible to noise in the training data. In this work, we aim at reducing intra-class noise with the help of graph filtering to improve the classification performance. Considered graphs are obtained by connecting samples of the training set that belong to a same class depending on the similarity of their representation in a latent space. We show that the proposed graph filtering methodology has the effect of asymptotically reducing intra-class variance, while maintaining the mean.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have been used recently for anomaly detection from images, where the anomaly scores are obtained by comparing the global difference between the input and generated image. However, the anomalies often appear in local areas of an image scene, and ignoring such information can lead to unreliable detection of anomalies.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views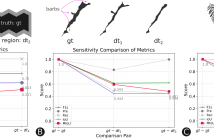
- Read more about Multiscale IoU: A Metric for Evaluation of Salient Object Detection with Fine Structures
- Log in to post comments
General-purpose object-detection algorithms often dismiss the fine structure of detected objects. This can be traced back to how their proposed regions are evaluated. Our goal is to renegotiate the trade-off between the generality of these algorithms and their coarse detections. In this work, we present a new metric that is a marriage of a popular evaluation metric, namely Intersection over Union (IoU), and a geometrical concept, called fractal dimension. We propose Multiscale IoU (MIoU) which allows comparison between the detected and ground-truth regions at multiple resolution levels.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about MICRO-EXPRESSION RECOGNITION BASED ON VIDEO MOTION MAGNIFICATION AND PRE-TRAINED NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
This paper investigates the effects of using video motion magnification methods based on amplitude and phase, respectively, to amplify small facial movements. We hypothesise that this approach will assist in the micro-expression recognition task. To this end, we apply the pre-trained VGGFace2 model with its excellent facial feature capturing ability to transfer learn the magnified micro-expression movement, then encode the spatial information and decode the spatial and temporal information by Bi-LSTM model.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Class-imbalanced classifiers using ensembles of Gaussian processes and Gaussian process latent variable models
- Log in to post comments
Classification with imbalanced data is a common and challenging problem in many practical machine learning problems. Ensemble learning is a popular solution where the results from multiple base classifiers are synthesized to reduce the effect of a possibly skewed distribution of the training set. In this paper, binary classifiers based on Gaussian processes are chosen as bases for inferring the predictive distributions of test latent variables. We apply a Gaussian process latent variable model where the outputs of the Gaussian processes are used for making the final decision.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about CNR-IEMN: a deep learning based approach to recognise Covid-19 from CT-scan
- Log in to post comments
SPGC_posterf.pptx
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Meta Ordinal Weighting Net For Improving Lung Nodule Classification
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about POINT OF CARE IMAGE ANALYSIS FOR COVID-19
- Log in to post comments
Early detection of COVID-19 is key in containing the pandemic. Disease detection and evaluation based on imaging is fast and cheap and therefore plays an important role in COVID-19 handling. COVID-19 is easier to detect in chest CT, however, it is expensive, non-portable, and difficult to disinfect, making it unfit as a point-of-care (POC) modality. On the other hand, chest X-ray (CXR) and lung ultrasound (LUS) are widely used, yet, COVID-19 findings in these modalities are not always very clear.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views