
- Read more about ADAPTIVE CONFIDENCE MULTI-VIEW HASHING FOR MULTIMEDIA RETRIEVAL
- Log in to post comments
The multi-view hash method converts heterogeneous data from multiple views into binary hash codes, which is one of the critical technologies in multimedia retrieval. However, the current methods mainly explore the complementarity among multiple views while lacking confidence in learning and fusion. Moreover, in practical application scenarios, the single-view data contains redundant noise. To conduct confidence learning and eliminate unnecessary noise, we propose a novel Adaptive Confidence Multi-View Hashing (ACMVH) method.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about PROBMCL: SIMPLE PROBABILISTIC CONTRASTIVE LEARNING FOR MULTI-LABEL VISUAL CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Multi-label image classification presents a challenging task in many domains, including computer vision and medical imaging. Recent advancements have introduced graph-based and transformer-based methods to improve performance and capture label dependencies. However, these methods often include complex modules that entail heavy computation and lack interpretability. In this paper, we propose Probabilistic Multi-label Contrastive Learning (ProbMCL), a novel framework to address these challenges in multi-label image classification tasks.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about A CONTRARIO PARADIGM FOR YOLO-BASED INFRARED SMALL TARGET DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Detecting small to tiny targets in infrared images is a challenging task in computer vision, especially when it comes to differentiating these targets from noisy or textured backgrounds. Traditional object detection methods such as YOLO
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about 2D Human Pose Estimation Calibration and Keypoint Visibility Classification
- Log in to post comments
The confidence scores of 2D pose estimation are widely utilized in various fields, including multi-view 3D human pose estimation, skeleton-based human tracking, human action recognition, human re-identification, etc. Despite widespread use, confidence scores from 2D pose estimation methods are unreliable in indicating the accuracy of estimation results, particularly in occlusion situations, i.e., keypoints with high confidence scores may have low accuracy and vice versa. To address this issue, we propose a new 2D human pose estimation calibration method in this paper.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about SEMANTIC DISTILLATION AND STRUCTURAL ALIGNMENT NETWORK FOR FAKE NEWS DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, the rapid proliferation of multi-modal fake news has posed potential harm across various sectors of society, making the detection of multi-modal fake news crucial. Most existing methods can not effectively reduce the redundant information and preserve both semantic and structural information. To address these problems, this paper proposes a semantic distillation and structural alignment (SDSA) network. We design an semantic distillation module for modality-specific features to preserve task-relevant semantic information and eliminate redundant information.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views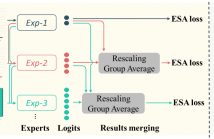
- Read more about ESA: Expert-and-Samples-Aware Incremental Learning under Longtail Distribution
- Log in to post comments
Most works in class incremental learning (CIL) assume disjoint sets of classes as tasks. Although a few works deal with overlapped sets of classes, they either assume a balanced data distribution or assume a mild imbalanced distribution. Instead, in this paper, we explore one of the understudied real-world CIL settings where (1) different tasks can share some classes but with new data samples, and (2) the training data of each task follows a long-tail distribution. We call this setting CIL-LT.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
- Read more about SSL-Net: A Synergistic Spectral and Learning-based Network for Efficient Bird Sound Classification
- Log in to post comments
Efficient and accurate bird sound classification is of importance for ecology, habitat protection and scientific research, as it plays a central role in monitoring the distribution and abundance of species. However, prevailing methods typically demand extensively labeled audio datasets and have highly customized frameworks, imposing substantial computational and annotation loads. In this study, we present an efficient and general framework called SSL-Net, which combines spectral and learned features to identify different bird sounds.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about SSL-Net: A Synergistic Spectral and Learning-based Network for Efficient Bird Sound Classification
- Log in to post comments
Efficient and accurate bird sound classification is of importance for ecology, habitat protection and scientific research, as it plays a central role in monitoring the distribution and abundance of species. However, prevailing methods typically demand extensively labeled audio datasets and have highly customized frameworks, imposing substantial computational and annotation loads. In this study, we present an efficient and general framework called SSL-Net, which combines spectral and learned features to identify different bird sounds.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views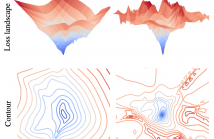
- Read more about Neural Network Training Strategy to Enhance Anomaly Detection Performance: A Perspective on Reconstruction Loss Amplification
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) is a widely adopted approach in industry due to rare anomaly occurrences and data imbalance. A desirable characteristic of an UAD model is contained generalization ability which excels in the reconstruction of seen normal patterns but struggles with unseen anomalies. Recent studies have pursued to contain the generalization capability of their UAD models in reconstruction from different perspectives, such as design of neural network (NN) structure and training strategy.
- Categories:
 283 Views
283 Views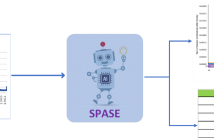
- Read more about SPASE: SPAtial Saliency Explanation for time series models
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
We have seen recent advances in the fields of Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Artificial intelligence (AI) that the models are becoming increasingly complex and large in terms of architecture and parameter size. These complex ML/DL models have beaten the state of the art in most fields of computer science like computer vision, NLP, tabular data prediction and time series forecasting, etc. With the increase in models’ performance, model explainability and interpretability has become essential to explain/justify model outcome, especially for business use cases.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views