
- Read more about Meta Ordinal Weighting Net For Improving Lung Nodule Classification
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Meta Ordinal Weighting Net For Improving Lung Nodule Classification
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about Task-aware neural architecture search
- Log in to post comments
The design of handcrafted neural networks requires a lot of time and resources. Recent techniques in Neural Architecture Search (NAS) have proven to be competitive or better than traditional handcrafted design, although they require domain knowledge and have generally used limited search spaces. In this paper, we propose a novel framework for neural architecture search, utilizing a dictionary of models of base tasks and the similarity between the target task and the atoms of the dictionary; hence, generating an adaptive search space based on the base models of the dictionary.
icassp_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Differential Convolution Feature Guided Deep Multi-Scale Multiple Instance Learning for Aerial Scene Classification
- Log in to post comments
Aerial image classification is challenging for current deep learning models due to the varied geo-spatial object scales and the complicated scene spatial arrangement. Thus, it is necessary to stress the key local feature response from a variety of scales so as to represent discriminative convolutional features. In this paper, we propose a deep multi-scale multiple instance learning (DMSMIL) framework to tackle the above challenges. Firstly, we develop a differential multi-scale dilated convolution feature extractor to exploit the different patterns from different scales.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Meta Ordinal Weighting Net For Improving Lung Nodule Classification
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views- Read more about TYPE I ATTACK FOR GENERATIVE MODELS
- Log in to post comments
Generative models are popular tools with a wide range of applications. Nevertheless, it is as vulnerable to adversarial samples as classifiers. The existing attack methods mainly focus on generating adversarial examples by adding imperceptible perturbations to input, which leads to wrong result. However, we focus on another aspect of attack, i.e., cheating models by significant changes. The former induces Type II error and the latter causes Type I error. In this paper, we propose Type I attack to generative models such as VAE and GAN.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about VISUAL RELATIONSHIP CLASSIFICATION WITH NEGATIVE-SAMPLE MINING
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces the application of a visual relationship classifier as a standalone system that is meant to be used with external detectors. Through these lens, we propose a training scheme that uses unannotated pairs of objects as negative samples in order to improve precision. The proposed network architecture incorporates common techniques presented in related state-of-the-art solutions with a novel positional encoding scheme.
estevao.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views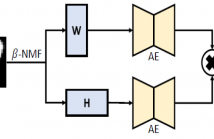
- Read more about Unsupervised learning from limited available data by β-NMF and dual autoencoder
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised Learning (UL) models are a class of Machine Learning (ML) which concerns with reducing dimensionality, data factorization, disentangling and learning the representations among the data. The UL models gain their popularity due to their abilities to learn without any predefined label, and they are able to reduce the noise and redundancy among the data samples.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about Pairwise Adjacency Matrix on Spatial Temporal Graph Convolution Network for Skeleton-based Two-Person Interaction Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks (ST-GCN) have achieved outstanding performances on human action recognition, however, it might be less superior on a two-person interaction recognition (TPIR) task due to the relationship of each skeleton is not considered. In this study, we present an improvement of the ST-GCN model that focused on TPIR by employing the pairwise adjacency matrix to capture the relationship of person-person skeletons (ST-GCN-PAM). To validate the effectiveness of the proposed ST-GCN-PAM model on TPIR, experiments were conducted on NTU RGB+D 120.
- Categories:
 112 Views
112 Views
- Read more about Bubblenet: A Disperse Recurrent Structure To Recognize Activities
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents an approach to perform human activity recognition in videos through the employment of a deep recurrent network, taking as inputs appearance and optical flow information. Our method proposes a novel architecture named BubbleNET, which is based on a recurrent layer dispersed into several modules (referred to as bubbles) along with an attention mechanism based on squeeze-and-excitation strategy, responsible to modulate each bubble contribution.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views