
- Read more about DEEP LEARNING BASED OFF-ANGLE IRIS RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Even with trained operators and cooperative subjects, it is still possible to capture off-angle iris images. Considering the recent demands for stand-off iris biometric systems and the trend towards ”on-the-move-acquisition”, off-angle iris recognition became a hot topic within the biometrics community. In this work, CNNs trained with the triplet loss function are applied to extract features for iris recognition.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views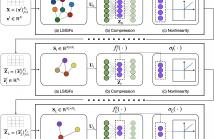
- Read more about Graph Convolutional Networks with Autoencoder-Based Compression and Multi-Layer Graph Learning
- Log in to post comments
The aim of this work is to propose a novel architecture and training strategy for graph convolutional networks (GCN). The proposed architecture, named as Autoencoder-Aided GCN (AA-GCN), compresses the convolutional features in an information-rich embedding at multiple hidden layers, exploiting the presence of autoencoders before the point-wise non-linearities. Then, we propose a novel end-to-end training procedure that learns different graph representations per each layer, jointly with the GCN weights and auto-encoder parameters.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views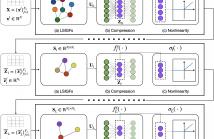
- Read more about Graph Convolutional Networks with Autoencoder-Based Compression and Multi-Layer Graph Learning
- Log in to post comments
The aim of this work is to propose a novel architecture and training strategy for graph convolutional networks (GCN). The proposed architecture, named as Autoencoder-Aided GCN (AA-GCN), compresses the convolutional features in an information-rich embedding at multiple hidden layers, exploiting the presence of autoencoders before the point-wise non-linearities. Then, we propose a novel end-to-end training procedure that learns different graph representations per each layer, jointly with the GCN weights and auto-encoder parameters.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views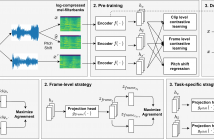
- Read more about SELF-SUPERVISED LEARNING METHOD USING MULTIPLE SAMPLING STRATEGIES FOR GENERAL-PURPOSE AUDIO REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
We propose a self-supervised learning method using multiple sampling strategies to obtain general-purpose audio representation. Multiple sampling strategies are used in the proposed method to construct contrastive losses from different perspectives and learn representations based on them. In this study, in addition to the widely used clip-level sampling strategy, we introduce two new strategies, a frame-level strategy and a task-specific strategy.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about NEAREST SUBSPACE SEARCH IN THE SIGNED CUMULATIVE DISTRIBUTION TRANSFORM SPACE FOR 1D SIGNAL CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a new method to classify 1D signals using the signed cumulative distribution transform (SCDT). The proposed method exploits certain linearization properties of
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about End-to-end Keyword Spotting using Neural Architecture Search and Quantization
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces neural architecture search (NAS) for the automatic discovery of end-to-end keyword spotting (KWS) models in limited resource environments. We employ a differentiable NAS approach to optimize the structure of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) operating on raw audio waveforms. After a suitable KWS model is found with NAS, we conduct quantization of weights and activations to reduce the memory footprint. We conduct extensive experiments on the Google speech commands dataset.
icassp_2022_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views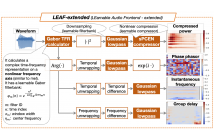
- Read more about AN INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PHASE FOR AUDIO CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
While log-amplitude mel-spectrogram has widely been used as the feature representation for processing speech based on deep learning, the effectiveness of another aspect of speech spectrum, i.e., phase information, was shown recently for tasks such as speech enhancement and source separation. In this study, we extensively investigated the effectiveness of including phase information of signals for eight audio classification tasks. We constructed a learnable front-end that can compute the phase and its derivatives based on a time-frequency representation with mel-like frequency axis.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Multitask Gaussian Process with Hierarchical Latent Interactions
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views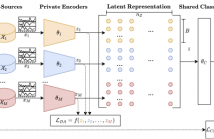
- Read more about DOMAIN-INVARIANT REPRESENTATION LEARNING FROM EEG WITH PRIVATE ENCODERS
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning based electroencephalography (EEG) signal processing methods are known to suffer from poor test-time generalization due to the changes in data distribution. This becomes a more challenging problem when privacy-preserving representation learning is of interest such as in clinical settings. To that end, we propose a multi-source learning architecture where we extract domain-invariant representations from dataset-specific private encoders.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views