
- Read more about 3D Facial Expression Recognition Based on Multi-View and Prior Knowledge Fusion
- Log in to post comments
MMSP2019.pdf
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about Deep Aggregation of Regional Convolutional Activations for Content Based Image Retrieval
- Log in to post comments
One of the key challenges of deep learning based image retrieval remains in aggregating convolutional activations into one highly representative feature vector. Ideally, this descriptor should encode semantic, spatial and low level information. Even though off-the-shelf pre-trained neural networks can already produce good representations in combination with aggregation methods, appropriate fine tuning for the task of image retrieval has shown to significantly boost retrieval performance.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views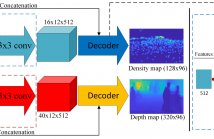
- Read more about DANET: DEPTH-AWARE NETWORK FOR CROWD COUNTING
- Log in to post comments
Image-based people counting is a challenging work due to the large scale variation problem caused by the diversity of distance between the camera and the person, especially in the congested scenes. To handle this problem, the previous methods focus on building complicated models and rely on labeling the sophisticated density maps to learn the scale variation implicitly. It is often time-consuming in data pre-processing and difficult to train these deep models due to the lack of training data.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about Photorealistic Image Synthesis for Object Instance Detection
- Log in to post comments
We present an approach to synthesize highly photorealistic images of 3D object models, which we use to train a convolutional neural network for detecting the objects in real images. The proposed approach has three key ingredients: (1) 3D object models are rendered in 3D models of complete scenes with realistic materials and lighting, (2) plausible geometric configuration of objects and cameras in a scene is generated using physics simulation, and (3) high photorealism of the synthesized images is achieved by physically based rendering.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about MULTIPLE INSTANCE DENSE CONNECTED CONVOLUTION NEURAL NETWORK FOR AERIAL IMAGE SCENE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
With the development of deep learning, many state-of-the-art natural image scene classification methods have demonstrated impressive performance. While the current convolution neural network tends to extract global features and global semantic information in a scene, the geo-spatial objects can be located at anywhere in an aerial image scene and their spatial arrangement tends to be more complicated. One possible solution is to preserve more local semantic information and enhance feature propagation.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about Fast 6dof Pose Estimation with Synthetic Textureless Cad Model for Mobile Applications
- Log in to post comments
Performance of 6DoF pose estimation techniques from RGB/RGB-D images has improved significantly with sophisticated deep learning frameworks. These frameworks require large-scale training data based on real/synthetic RGB/RGB-D information. Difficulty of obtaining adequate training data has limited the scope of these frameworks for ubiquitous application areas. Also, fast pose estimation at inference time often requires high-end GPU(s) that restricts the scope for its application in mobile hardware.
- Categories:
 217 Views
217 Views
Current face detection concentrates on detecting tiny faces and severely occluded faces. Face analysis methods, however, require a good localization and would benefit greatly from some rotation information. We propose to predict a face direction vector (FDV), which provides the face size and orientation and can be learned by a common object detection architecture better than the traditional bounding box. It provides a more consistent definition of face location and size. Using the FDV is promising for all succeeding face analysis methods.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Unconstrained Flood Event Detection Using Adversarial Data Augmentation
- Log in to post comments
Nowadays, the world faces extreme climate changes, resulting in an increase of natural disaster events and their severities. In these conditions, the necessity of disaster information management systems has become more imperative. Specifically, in this paper, the problem of flood event detection from images with real-world conditions is addressed. That is, the images may be taken in several conditions, including day, night, blurry, clear, foggy, rainy, different lighting conditions, etc. All these abnormal scenarios significantly reduce the performance of the learning algorithms.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about Rotation-Invariant CNN using scattering transform for image classification
- Log in to post comments
ICIP_v1.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Generation of head models for brain stimulation using deep convolution networks
- Log in to post comments
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive clinical technique used for treatment of several neurological diseases such as depression, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. However, it is always challenging to accurately adjust the electric field on different specific brain regions due to the requirement of several stimulation parameters’ optimizations.
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views