
A flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, GlobalSIP is structured around coherent symposia that explore new and emerging developments in the field, while maintaining a format that encourages accessibility to interested researchers and fosters interaction and cross-pollination of ideas.

- Read more about PHYSICAL LAYER SECURITY GAME WITH FULL-DUPLEX PROACTIVE EAVESDROPPER
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Third dimension for measurement of multi user massive MIMO channels based on LTE advanced downlink
- Log in to post comments
We characterize third-dimension (3D) of channel measurements based on two dimension channel model with fully synchronize
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Robust Energy-Efficient Transmit Design for MISOME Wiretap Channels
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers an energy-efficient transmit design in a general multiple-input single-output multiple-eavesdropper (MISOME) wiretap channel. Specifically, a transmitter sends one confidential message to a legitimate receiver, which must be kept perfectly secure from several external multi-antenna eavesdroppers. Assuming imperfect channel state information (CSI) at the transmitter, our goal is to design the input transmit covariance, such that the worst-case secrecy energy efficiency (WC-SEE) is maximized, subject to the quality of service (QoS) and total transmit power constraints.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about I-LoViT: Indoor Localization by Vibration Tracking
- Log in to post comments
Signal processing techniques can create new applications for the data captured by existing sensor systems. Decades old sensor technology for monitoring the structural health of a building can serve a new role as a novel source of indoor localization data. Specifically, when a person's footstep-generated floor vibrations can be detected and located then it is possible to locate persons moving within a building. This emergent cyber-physical system holds the potential for an ambient localization service.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Action Classification from Motion Capture Data using Topological Data Analysis
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a novel framework for activity recognition from 3D motion capture data using topological data analysis (TDA). We extract point clouds describing the oscillatory patterns of body joints from the principal components of their time series using Taken's delay embedding. Topological persistence from TDA is exploited to extract topological invariants of the constructed point clouds. We propose a feature extraction method from persistence diagrams in order to generate robust low dimensional features used for classification of different activities.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views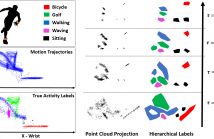
- Read more about Hierarchical Activity Clustering Analysis for Robust Graphical Structure Recovery
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we propose a hierarchical activity clustering methodology which incorporates the use of topological persistence analysis. Our clustering methodology captures the hierarchies present in the data and is therefore able to show the dependencies that exist between these activities. We make use of an aggregate persistence diagram to select robust graphical structures present within the dataset. These models are stable over a bound and provide accurate classification results.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about D-OAMP: A Denoising-based Signal Recovery Algorithm for Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Low-Density Spatial RS Design and Channel Estimation for FDD Massive Full-Dimensional MIMO Systems
- Log in to post comments
A low-density spatial downlink reference signal (LDS-RS) design is proposed for frequency-division duplex (FDD) massive full-dimensional multiple-input multiple-output (FD-MIMO) systems. By exploiting the spatial correlation between the channels of different antennas, this scheme can efficiently reduce the downlink RS overhead and therefore enhances the achievable spectral efficiency significantly.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about ON THE TRADEOFF BETWEEN RESOLUTION AND AMBIGUITIES FOR NON-UNIFORM LINEAR ARRAYS
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views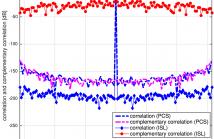
- Read more about Construction of Complementary Sets of Sequences with Low Aperiodic Correlation and Complementary Correlation
- Log in to post comments
The construction of complementary sets of unimodular sequences of length N, with low correlation and complementary correlation coefficients is addressed. The design criterion is based on the minimisation of a cost function that penalizes the integrated side lobe as well as the sum of the complementary correlations of the sequences in the set. Numerical solution to the proposed cost function is obtained using conventional optimization methods.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views