
A flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, GlobalSIP is structured around coherent symposia that explore new and emerging developments in the field, while maintaining a format that encourages accessibility to interested researchers and fosters interaction and cross-pollination of ideas.

- Read more about DETECTION OF SPOKEN WORDS IN NOISE: COMPARISON OF HUMAN PERFORMANCE TO MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we are interested in assessing the optimality of the human auditory system, when the input stimuli is natural speech that is affected by additive noise. In order to do this, we consider the DANTALE II listening test paradigm of Wagener et al., which has been used to evaluate the intelligibility of noisy speech by exposing human listeners to a selection of constructed noisy sentences. Inspired by this test, we propose a simple model for the communication and classification of noisy speech that takes place in the test.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about DYNAMIC SUBARRAY ARCHITECTURE FOR WIDEBAND HYBRID PRECODING IN MILLIMETER WAVE MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Hybrid precoding architectures can address the trade-off between achievable spectral efficiency and power consumption in large-scale MIMO systems. Most of the prior work on hybrid precoding focused on narrowband channels and assumed fully-connected hybrid architectures. In this paper, a closed-form solution for OFDM-based wideband hybrid precoding is developed for both fully-connected and subarray architectures in frequency selective channels. The closed form solution provides useful insights into how hybrid subarray structures should be designed.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about DETECTION DIVERSITY OF SPATIO-TEMPORAL DATA USING PITMAN’S EFFICIENCY FOR LOW SNR REGIMES
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we use Pitman’s efficiency to characterize the diversity of a spatio-temporal distributed detection system. Pitman’s efficiency directly measures the detection ability of the data at low signal to noise ratios (SNRs). We study how the
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about A Hierarchical Approach to Event Discovery from Single Images using MIL Framework
- Log in to post comments
In this poster, we propose to face the problem of event detec/on from single
images, by exploi/ng both background informaAon oNen containing revealing
contextual clues and details, which are salient for recognizing the event. Such
details are visual objects criAcal to understand the underlying event depicted in
the image and were recently defined in the literature as ”event-saliency”.
Adop/ng the MulAple-Instance Learning (MIL) paradigm we propose a
hierarchical approach analyzing first the en/re picture and then refining the
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Out-of-label Suppression Dictionary Learning with Cluster Regularization
- Log in to post comments
This paper addresses the problem of learning a discriminative dictionary from training signals. Given a structured dictionary, each atom of which has its corresponding label, one signal should be mainly constructed by its closely associated atoms. Besides the representations for the same class ought to be very close to form a cluster. Thus we present out-of-label suppression dictionary model with cluster regularization to amplify the discriminative power. Upon out-of-label suppression, we don't adopt $l_0$-norm or $l_1$-norm for regularization.
GlobalSIP 2016.pdf
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views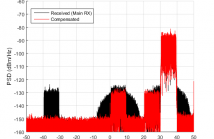
- Read more about REFERENCE RECEIVER ENABLED DIGITAL CANCELLATION OF NONLINEAR OUT-OF-BAND BLOCKER DISTORTION IN WIDEBAND RECEIVERS
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes digital cancellation of nonlinear distortion originating from out-of-band blocking carriers and induced by the analog front-end nonlinearities in direct-conversion receivers (RXs). The cancellation is enabled by employing an additional reference RX for capturing these blockers. In addition, cancellation of mirror-frequency interference is targeted. The feed-forward cancellation of nonlinear distortion is blindly adaptive without any a priori information of the received signal or the nonlinearity characteristics of the RX.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Onsager-corrected deep learning for sparse linear inverse problems
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning has gained great popularity due to its widespread success on many inference problems. We consider the application of deep learning to the sparse linear inverse problem encountered in compressive sensing, where one seeks to recover a sparse signal from a few noisy linear measurements. In this paper, we propose two novel neural-network architectures that decouple prediction errors across layers in the same way that the approximate message passing (AMP) algorithms decouple them across iterations: through Onsager correction.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 Views
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Distributed Sequence Prediction: A consensus+innovations approach
- Log in to post comments
This paper focuses on the problem of distributed sequence
prediction in a network of sparsely interconnected agents,
where agents collaborate to achieve provably reasonable
predictive performance. An expert assisted online learning
algorithm in a distributed setup of the consensus+innovations
form is proposed, in which the agents update their weights
for the experts’ predictions by simultaneously processing the
latest network losses (innovations) and the cumulative losses
obtained from neighboring agents (consensus). This paper
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Optimal Stochastic Power Control with Compressive CSI Acquisition for Cloud-RAN
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers the channel state information (CSI) acquisition and exploitation problem in cloud radio access networks (Cloud-RAN). A novel CSI acquisition method, called compressive CSI acquisition, is adopted to effectively reduce the CSI signaling overhead by obtaining instantaneous coefficients of only a subset of all the channel links.To deal with the uncertainty in available CSI, we propose a stochastic power control (SPC) framework, which is a highly intractable joint chance constrained program (JCCP).
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views