
A flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, GlobalSIP is structured around coherent symposia that explore new and emerging developments in the field, while maintaining a format that encourages accessibility to interested researchers and fosters interaction and cross-pollination of ideas.

- Read more about GlobalSIP_Recover from Tracking Failure_KEHE
- Log in to post comments
Numerous trackers have been proposed in recent years with considerable success. But few trackers can cope with all scenarios without failures. It is very difficult to design a tracker robust enough to keep off tracking failure. As failure is inevitable, we propose a framework to correct tracker, verify failure, predict object position and re-detect object. The original model of the first frame is used to correct the tracker. Then, the confidence of tracking is used to verify tracking failure.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views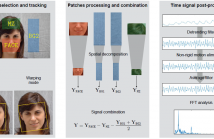
Measuring the Heart Rate (HR) plays an important role in the description of human physiological and psychological state, due to its relationship with cognitive/emotional factors such as attention effort, stress or arousal. For this reason, remote methodologies for HR measurements have recently been investigated to find a reliable and cost-effective methodology. Our work aims at the following:
• Development of a novel technique for remote HR estimation
• Comparison of the proposed method with the state of the art on a common dataset
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Achieving High Throughput with Predictive Resource Allocation
- Log in to post comments
Big data analytics makes predicting human behavior possible, but it is unclear how to exploit the predictable information for improving performance of wireless networks. In this paper, we investigate the potential of predictive resource allocation in supporting high throughput by exploiting excess resources. To this end, we assume that the requests and trajectories of mobile users and the average resource usage status of base stations can be predicted within a window.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about ROBUST ONLINE MULTI-OBJECT TRACKING BASED ON KCF TRACKERS AND REASSIGNMENT
- Log in to post comments
There is a big challenge in online multi-object tracking-by-detection, which caused by frequent occlusions, false alarms or miss detections and other factors. In this paper, we pro-posed an improved fast online multi-object tracking method through taking into account the results of multiple single-object trackers and detections synthetically. To solve the fixed scale problem of conventional kernelized correlation filter in single-object tracker we used, trackers are associated with de-tections based on position and size and then an adaptive mech-anism of trackers is established.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about CACHING POLICY OPTIMIZATION FOR RATE ADAPTIVE VIDEO STREAMING
- Log in to post comments
FD_Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Approximate Support Recovery of Atomic Line Spectral Estimation: A Tale of Resolution and Precision
- Log in to post comments
This work investigates the parameter estimation performance of super-resolution line spectral estimation using atomic norm minimization. The focus is on analyzing the algorithm's accuracy of inferring the frequencies and complex magnitudes from noisy observations. When the Signal-to-Noise Ratio is reasonably high and the true frequencies are separated by $O(\frac{1}{n})$, the atomic norm estimator is shown to localize the correct number of frequencies, each within a neighborhood of size $O(\sqrt{\frac{\log n}{n^3}} \sigma)$ of one of the true frequencies.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Approximate Support Recovery of Atomic Line Spectral Estimation: A Tale of Resolution and Precision
- Log in to post comments
This work investigates the parameter estimation performance of super-resolution line spectral estimation using atomic norm minimization. The focus is on analyzing the algorithm's accuracy of inferring the frequencies and complex magnitudes from noisy observations. When the Signal-to-Noise Ratio is reasonably high and the true frequencies are separated by $O(\frac{1}{n})$, the atomic norm estimator is shown to localize the correct number of frequencies, each within a neighborhood of size $O(\sqrt{\frac{\log n}{n^3}} \sigma)$ of one of the true frequencies.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views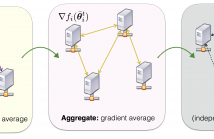
- Read more about A Projection-free Decentralized Algorithm for Non-convex Optimization
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers a decentralized projection free algorithm for non-convex optimization in high dimension. More specifically, we propose a Decentralized Frank-Wolfe (DeFW)
algorithm which is suitable when high dimensional optimization constraints are difficult to handle by conventional projection/proximal-based gradient descent methods. We present conditions under which the DeFW algorithm converges to a stationary point and prove that the rate of convergence is as fast as ${\cal O}( 1/\sqrt{T} )$, where
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Neighborhood-Preserving Translations on Graphs
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Downlink Resource Allocation for Multichannel TDMA Visible Light Communications
- Log in to post comments
Optical wireless communications (OWC) in general
and resource allocation in OWC networks particularly have
gained lots of attention recently. In this work, we consider the
resource allocation problem of a visible light communication
downlink transmission system based on time division multiple
access with the objective of maximizing spectral efficiency (SE).
As for the operational conditions, we impose constraints on
the average optical intensity, the energy consumption and the
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views