ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2016 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics.
- Read more about A MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD-BASED UNSCENTED KALMAN FILTER FOR MULTIPATH MITIGATION IN A MULTI-CORRELATOR BASED GNSS RECEIVER
- Log in to post comments
In complex environments, the presence or absence of multipath signals not only depends on the relative motion between the GNSS receiver and navigation satellites, but also on the environment where the receiver is located. Thus it is difficult to use a specific propagation model to accurately capture the dynamics of multipath signal parameters when the GNSS receiver is moving in urban canyons or other severe obstructions. This paper introduces a statistical model for the line-of-sight and multipath signals received by a GNSS receiver.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
Automated objective methods of audio evaluation are fast, cheap, and require little effort by the investigator. However, objective evaluation methods do not exist for the output of all audio processing algorithms, often have output that correlates poorly with human quality assessments, and require ground truth data in their calculation. Subjective human ratings of audio quality are the gold standard for many tasks, but are expensive, slow, and require a great deal of effort to recruit subjects and run listening tests.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views- Read more about Distributed Generalized Likelihood Ratio Tests: Fundamental Limits and Tradeoffs
- Log in to post comments
This paper focuses on the problem of distributed composite
hypothesis testing in a network of sparsely interconnected
agents, in which only a small section of the field modeling
parametric alternatives is observable at each agent. A recursive
generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) type algorithm
in a distributed setup of the consensus-plus-innovations form
is proposed, in which the agents update their parameter estimates
and decision statistics by simultaneously processing
the latest sensed information (innovations) and information
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Analysis of p-norm Regularized Subproblem Minimization for Sparse Photon-Limited Image Recovery
- Log in to post comments
Critical to accurate reconstruction of sparse signals from low-dimensional low-photon count observations is the solution of nonlinear optimization problems that promote sparse solutions. In this work, we explore recovering high-resolution sparse signals from low-resolution measurements corrupted by Poisson noise using a gradient-based optimization approach with non-convex regularization. In particular, we analyze zero-finding methods for solving the p-norm regularized minimization subproblems arising from a sequential quadratic approach.
ICASSP2016.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about REAL-TIME DATA SELECTION AND ORDERING FOR COGNITIVE BIAS MITIGATION
- Log in to post comments
Abstract
We consider the problem of selecting and ordering a subset of N' out of N observations to be presented to a human being in the context of a binary hypothesis testing problem. We restrict our attention to i.i.d. Gaussian observations. We propose an extension of the approximate subset sum algorithm,and show that it can be used to solve the problem with polynomial complexity. Furthermore, we show that the solution yields near optimal detection performance when compared to the case where all N observations are optimally processed.
ICASSP_16.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Dirichlet process mixture models for time-dependent clustering
- Log in to post comments
In many problems of signal processing, an important task is the classification of data. A group of methods that has attracted much interest for this purpose are the nonparametric Bayesian methods, and in particular, those based on the Dirichlet process. A useful metaphor for various generalizations of the Dirichlet process has been the Chinese restaurant process. Often the task of classification must be carried out in a sequential manner, and to that end the concepts from Bayesian non-parametrics cannot be applied straightforwardly.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views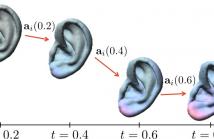
- Read more about Generating a Morphable Model of Ears
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes the generation of a morphable model for external ear shapes. The aim for the morphable model is to characterize an ear shape using only a few parameters in order to assist the study of morphoacoustics. The model is derived from a statistical analysis of a population of 58 ears from the SYMARE database. It is based upon the framework of large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping (LDDMM) and the vector space that is constructed over the space of initial momentums describing the diffeomorphic transformations.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views- Read more about Direction of Arrival Estimation in MIMO Radar Systems With Nonlinear Reflectors
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about On The Importance of Harmonic Phase Modification for Improved Speech Signal Reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views