
- Read more about Adversarial variational Bayes methods for Tweedie compound Poisson mixed models
- Log in to post comments
The Tweedie Compound Poisson-Gamma model is routinely used for modeling non-negative continuous data with a discrete probability mass at zero. Mixed models with random effects account for the covariance structure related to the grouping hierarchy in the data. An important application of Tweedie mixed models is pricing the insurance policies, e.g. car insurance. However, the intractable likelihood function, the unknown variance function, and the hierarchical structure of mixed effects have presented considerable challenges for drawing inferences on Tweedie.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about UNMIXING DYNAMIC PET IMAGES: COMBINING SPATIAL HETEROGENEITY AND NON-GAUSSIAN NOISE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views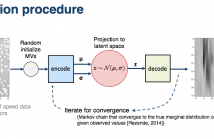
- Read more about Missing Data In Traffic Estimation: A Variational Autoencoder Imputation Method
- Log in to post comments
Road traffic forecasting systems are in scenarios where sensor or system failure occur. In those scenarios, it is known that missing values negatively affect estimation accuracy although it is being often underestimate in current deep neural network approaches. Our assumption is that traffic data can be generated from a latent space. Thus, we propose an online unsupervised data imputation method based on learning the data distribution using a variational autoencoder (VAE).
- Categories:
 208 Views
208 Views
- Read more about ENLLVM: Ensemble based Nonlinear Bayesian Filtering using Linear Latent Variable Models
- Log in to post comments
Real-time nonlinear Bayesian filtering algorithms are overwhelmed by data volume, velocity and increasing complexity of computational models. In this paper, we propose a novel ensemble based nonlinear Bayesian filtering approach which only requires a small number of simulations and can be applied to high-dimensional systems in the presence of intractable likelihood functions.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Variational and Hierarchical Recurrent Autoencoder
- Log in to post comments
Despite a great success in learning representation for image data, it is challenging to learn the stochastic latent features from natural language based on variational inference. The difficulty in stochastic sequential learning is due to the posterior collapse caused by an autoregressive decoder which is prone to be too strong to learn sufficient latent information during optimization. To compensate this weakness in learning procedure, a sophisticated latent structure is required to assure good convergence so that random features are sufficiently captured for sequential decoding.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about A Learning Approach for Optimal Codebook Selection in Spatial Modulation Systems
- Log in to post comments
In spatial modulation (SM) systems that utilize multiple transmit antennas/patterns with a single radio front-end, we propose a learning approach to predict the average symbol error rate (SER) conditioned on the instantaneous channel state. We show that the predicted SER can be used to lower the average SER over Rayleigh fading channels by selecting the optimal codebook in each transmission instance.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Bayesian Learning based Millimeter-Wave Sparse Channel Estimation with Hybrid Antenna Arrays
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of millimeter-wave (mmWave) channel estimation with a hybrid digital-analog two-stage beamforming structure. A radio frequency (RF) chain excites a dedicated set of antenna subarrays. To compensate for the severe path loss, known training signals are beamformed and swept to scan the angular space. Since the mmWave channels typically exhibit sparsity, the channel response can usually be expressed as a linear combination of a small number of scattering clusters.
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views
- Read more about CLUSTERING-GUIDED GP-UCB FOR BAYESIAN OPTIMIZATION
- Log in to post comments
Bayesian optimization is a powerful technique for finding extrema of an objective function, a closed-form expression of which is not given but expensive evaluations at query points are available. Gaussian Process (GP) regression is often used to estimate the objective function and uncertainty estimates that guide GP-Upper Confidence Bound (GP-UCB) to determine where next to sample from the objective function, balancing exploration and exploitation. In general, it requires an auxiliary optimization to tune the hyperparameter in GP-UCB, which is sometimes not easy to carry out in practice.
- Categories:
 102 Views
102 Views
- Read more about INFORMATION FUSION USING PARTICLES INTERSECTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about A FAST BAYESIAN ALGORITHMIC ENHANCEMENT FOR REAL TIME BIT ERROR RATIO TEST (BERT)
- Log in to post comments
Continuous, real-time bit error ratio (BER) test of modern communication and storage channels is a ubiquitous problem: the noises tend to vary in space and time, and are difficult to fully characterize offline. Traditional method requires time consuming accumulation of samples for which Bayesian method has shown its promise in alleviating by incorporating a priori knowledge. However, the method has so far depended on a simplistic linear search algorithm that suffers from long running time which defeats the purpose of sample reduction.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views