- Read more about CLASSIFIER CASCADE TO AID IN DETECTION OF EPILEPTIFORM TRANSIENTS IN INTERICTAL EEG
- Log in to post comments
Presence of interictal epileptiform discharges (IED) in the electroencephalogram (EEG) is indicative of epilepsy. Automated
software for annotating EEGs of Patients with suspected epilepsy is substantial for diagnosis and management of epilepsy.
A large amount of data is needed for training and evaluating the performance of an effective IED detection system. IEDs occur
infrequently in the EEG of most patients, hence, interictal EEG recordings contain mostly background waveforms. As the first
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Ear-EEG for Detecting Inter-brain Synchronisation in Continuous Cooperative Multi-person Scenarios
- Log in to post comments
The hyperscanning method simultaneously acquires and relates
cerebral data from two participants while performing
cooperative activities. The aim of this work is to evaluate
the performance of our novel EEG recording concept,
termed ear-EEG, against on-scalp EEG as an alternative,
user-friendly data acquisition approach for hyperscanning, in
the task of identifying the most robust, EEG subbands for
inter-individual neuronal synchrony detection in cooperative
multi-player gaming. This is achieved through the estimation
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about UNOBTRUSIVE MONITORING OF SPEECH IMPAIRMENTS OF PARKINSON'S DISEASE PATIENTS THROUGH MOBILE DEVICES
- Log in to post comments
Parkinson’s disease (PD) produces several speech impairments in the patients. Automatic classification of PD patients is performed considering speech recordings collected in non- controlled acoustic conditions during normal phone calls in a unobtrusive way. A speech enhancement algorithm is applied to improve the quality of the signals. Two different classification approaches are considered: the classification of PD patients and healthy speakers and a multi-class experiment to classify patients in several stages of the disease.
icassp.pdf
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about Cognitive Analysis of Working Memory Load from EEG, by a Deep Recurrent Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
One of the common modalities for observing mental activity is electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. However, EEG recording is highly susceptible to various sources of noise and to inter-subject differences. In order to solve these problems, we present a deep recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture to learn robust features and predict the levels of the cognitive load from EEG recordings. Using a deep learning approach, we first transform the EEG time series into a sequence of multispectral images which carries spatial information.
Kuanar_ICASSP-2018.pdf
- Categories:
 433 Views
433 Views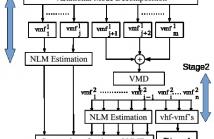
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE NON-LOCAL SIMILARITY PRESENT IN VARIATIONAL MODE FUNCTIONS FOR EFFECTIVE ECG DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
In the presented work, noisy ECG signal is decomposed into variational mode functions (VMFs) using variational mode decomposition (VMD) technique. The decomposed VMFs represents the different frequency band of the noisy ECG signal. The non-local similarity present in each VMFs were exploited using NLM estimation for effective ECG denoising. The two-stage VMD decomposition and NLM estimation process is performed on different set of VMFs at both stages. The proposed method is tested upon MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views