
- Read more about Enhancing the Reliability of Large-Scale Multiuser Molecular Communication Systems
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Effective Noise Removal and Unified Model of Hybrid Feature Space Optimization for Automated Cardiac Anomaly Detection using phonocardiogarm signals
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present completely automated cardiac anomaly detection for remote screening of cardio-vascular abnormality using Phonocardiogram (PCG) or heart sound signal. Even though PCG contains significant and vital cardiac health information and cardiac abnormality signature, the presence of substantial noise does not guarantee highly effective analysis of cardiac condition. Our proposed method intelligently identifies and eliminates noisy PCG signal and consequently detects pathological abnormality condition. We further present a unified model of hybrid feature selection method.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about EPILEPTIC STATE SEGMENTATION WITH TEMPORAL-CONSTRAINED CLUSTERING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views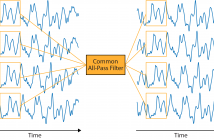
- Read more about Time-Varying Delay Estimation using Common Local All-Pass Filters with Application to Surface Electromyography
- Log in to post comments
Estimation of conduction velocity (CV) is an important task in the analysis of surface electromyography (sEMG). The problem can be framed as estimation of a time-varying delay (TVD) between electrode recordings. In this paper we present an algorithm which incorporates information from multiple electrodes into a single TVD estimation. The algorithm uses a common all-pass filter to relate two groups of signals at a local level.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about An Ensemble Learning Approach To Detect Epileptic Seizures From Long Intracranial EEG Recordings
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Towards online spike sorting for high-density neural probes using discriminative template matching with suppression of interfering spikes
- Log in to post comments
Spike sorting is the process of assigning each detected neuronal spike in an extracellular recording to its putative source neuron. A linear filter design is proposed where the filter output allows for threshold-based spike sorting of high-density neural probe data. The proposed filter design is based on optimizing the signal-to-peak-interference ratio for each detectable neuron in a data-driven way.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about A PRAGMATIC AUTHENTICATION SYSTEM USING ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
EEG-based authentication is an emerging research field. In this work, a realistic authentication system using Electroencephalography signals, was developed aiming to show that brain signals contain sufficient information to be used in security systems. The dataset used was composed of 29 users on 4 different days via the cheap Neurosky Mindwave headset with a single dry electrode, and 10 users on 3 different days via Emotiv with 14 electrodes. Various techniques, features, and algorithms were examined to achieve the highest security.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Stochastic Dynamical Systems Based Latent Structure Discovery in High-dimensional Time Series
- Log in to post comments
The brain encodes information by neural spiking activities, which can be described by time series data as spike counts. Latent Vari- able Models (LVMs) are widely used to study the unknown factors (i.e. the latent states) that are dependent in a network structure to modulate neural spiking activities. Yet, challenges in performing experiments to record on neuronal level commonly results in rela- tively short and noisy spike count data, which is insufficient to de- rive latent network structure by existing LVMs. Specifically, it is difficult to set the number of latent states.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY STATES OF THE BRAIN USING RESTRICTED BOLTZMANN MACHINES
- Log in to post comments
Recent work on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) suggests that functional connectivity (FC) is dynamic. A variety of machine learning and signal processing tools have been applied to the study of dynamic functional connectivity networks (dFCNs) of the brain, by identifying a small number of network states that describe the dynamics of connectivity during rest. Recently, deep learning (DL) methods have been applied to neuroimaging data for learning generative models.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Poster for ICCASP 2018
- Log in to post comments
Identification of cell subclasses using single-cell RNA-Sequencing (scRNA-Seq) data is of paramount importance since it uncovers the hidden biological processes within the cell population. While the nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) model has been reported to be effective in various unsupervised clustering tasks, it may still produce inappropriate results for some scRNA-Seq datasets with heterogeneous structures. In this paper, we propose the use of an orthogonally constrained NMF (ONMF) model for the subclass identification problem of scRNA-Seq datasets.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views