- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation

- Read more about RECOGNIZING MINIMAL FACIAL SKETCH BY GENERATING PHOTOREALISTIC FACES WITH THE GUIDANCE OF DESCRIPTIVE ATTRIBUTES
- Log in to post comments
Cross-modal sketch-photo recognition is of vital importance
in law enforcement and public security. Most existing methods
are dedicated to bridging the gap between the low-level
visual features of sketches and photo images, which is limited
due to intrinsic differences in pixel values. In this paper, based
on the intuition that sketches and photo images are highly correlated
in the semantic domain, we propose to jointly utilize
the low-level visual features and high-level facial attributes to
xiao_yang.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Image Restoration with Deep Generative Models
- Log in to post comments
Many image restoration problems are ill-posed in nature, hence, beyond the input image, most existing methods rely on a carefully engineered image prior, which enforces some local image consistency in the recovered image. How tightly the prior assumptions are fulfilled has a big impact on the resulting task performance. To obtain more flexibility, in this work, we proposed to design the image prior in a data-driven manner. Instead of explicitly defining the prior, we learn it using deep generative models.
- Categories:
 223 Views
223 Views
- Read more about SEQUENTIAL ADAPTIVE DETECTION FOR IN-SITU TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY (TEM)
- Log in to post comments
We develop new efficient online algorithms for detecting transient sparse signals in TEM video sequences, by adopting the recently developed framework for sequential detection jointly with online convex optimization [1]. We cast the problem as detecting an unknown sparse mean shift of Gaussian observations, and develop adaptive CUSUM and adaptive SSRS procedures, which are based on likelihood ratio statistics with post-change mean vector being online maximum likelihood estimators with ℓ1. We demonstrate the meritorious performance of our algorithms for TEM imaging using real data.
icassp2018_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views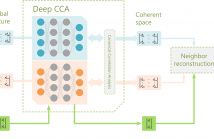
- Read more about LOW RESOLUTION FACE RECOGNITION AND RECONSTRUCTION VIA DEEP CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
Low-resolution (LR) face identification is always a challenge in computer vision. In this paper, we propose a new LR face recognition and reconstruction method using deep canonical correlation analysis (DCCA). Unlike linear CCA-based methods, our proposed method can learn flexible nonlinear representations by passing LR and high-resolution (HR) image principal component features through multiple stacked layers of nonlinear transformation.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Block-coordinate proximal algorithms for scale-free texture segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Texture segmentation still constitutes an on-going challenge, especially when processing large-size images.
Recently, procedures integrating a scale-free (or fractal)wavelet-leader model allowed the problem to be reformulated in a convex optimization framework by including a TV penalization. In this case, the TV penalty plays
icassp2018.pdf
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Image Segmentation by Backpropagation
- Log in to post comments
We investigate the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for unsupervised image segmentation. As in the case of supervised image segmentation, the proposed CNN assigns labels to pixels that denote the cluster to which the pixel belongs. In the unsupervised scenario, however, no training images or ground truth labels of pixels are given beforehand. Therefore, once when a target image is input, we jointly optimize the pixel labels together with feature representations while their parameters are updated by gradient descent.
- Categories:
 875 Views
875 Views
- Read more about SUPER WIDE REGRESSION NETWORK FOR UNSUPERVISED CROSS-DATABASE FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised cross-database facial expression recognition(FER) is a challenging problem, in which the training and testing samples belong to different facial expression databases. For this reason, the training (source) and testing (target) facial expression samples would have different feature distributions and hence the performance of lots of existing FER methods may decrease.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about IMAGE REPRESENTATION USING SUPERVISED AND UNSUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS ON COMPLEX DOMAIN
- Log in to post comments
Matrix factorization (MF) and its extensions have been intensively studied in computer vision and machine learning. In this paper, unsupervised and supervised learning methods based on MF technique on complex domain are introduced. Projective complex matrix factorization (PCMF) and discriminant projective complex matrix factorization (DPCMF) present two frameworks of projecting complex data to a lower dimension space. The optimization problems are formulated as the minimization of the real-valued functions of complex variables.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about IMAGE REPRESENTATION USING SUPERVISED AND UNSUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS ON COMPLEX DOMAIN
- Log in to post comments
Matrix factorization (MF) and its extensions have been intensively studied in computer vision and machine learning. In this paper, unsupervised and supervised learning methods based on MF technique on complex domain are introduced. Projective complex matrix factorization (PCMF) and discriminant projective complex matrix factorization (DPCMF) present two frameworks of projecting complex data to a lower dimension space. The optimization problems are formulated as the minimization of the real-valued functions of complex variables.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views- Read more about IMAGE REPRESENTATION USING SUPERVISED AND UNSUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS ON COMPLEX DOMAIN
- Log in to post comments
Matrix factorization (MF) and its extensions have been intensively studied in computer vision and machine learning. In this paper, unsupervised and supervised learning methods based on MF technique on complex domain are introduced. Projective complex matrix factorization (PCMF) and discriminant projective complex matrix factorization (DPCMF) present two frameworks of projecting complex data to a lower dimension space. The optimization problems are formulated as the minimization of the real-valued functions of complex variables.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views