- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation
- Read more about ICIP 2017 Poster Paper 3060
- Log in to post comments
Top-down attention plays an important role in guidance of human attention in real-world scenarios, but less efforts in computational modeling of visual attention has been put on it. Inspired by the mechanisms of top-down attention in human visual perception, we propose a multi-layer linear model of top-down attention to modulate bottom-up saliency maps actively. The first layer is a linear regression model which combines the bottom-up saliency maps on various visual features and objects.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views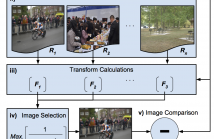
- Read more about Spotting the Difference: Context Retrieval and Analysis for Improved Forgery Detection and Localization
- Log in to post comments
As image tampering becomes ever more sophisticated and commonplace, the need for image forensics algorithms that can accurately and quickly detect forgeries grows. In this paper, we revisit the ideas of image querying and retrieval to provide clues to better localize forgeries. We propose a method to perform large-scale image forensics on the order of one million images using the help of an image search algorithm and database to gather contextual clues as to where tampering may have taken place.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views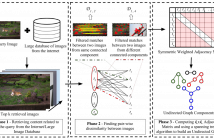
- Read more about U-Phylogeny: Undirected Provenance Graph Construction in the Wild
- Log in to post comments
Deriving relationships between images and tracing back their history of modifications are at the core of Multimedia Phylogeny solutions, which aim to combat misinformation through doctored visual media. Nonetheless, most recent image phylogeny solutions cannot properly address cases of forged composite images with multiple donors, an area known as multiple parenting phylogeny (MPP). This paper presents a preliminary undirected graph construction solution for MPP, without any strict assumptions.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about FEATURE SAMPLING STRATEGIES FOR ACTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views- Read more about LOOSECUT: INTERACTIVE IMAGE SEGMENTATION WITH LOOSELY BOUNDED BOXES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 ViewsAlthough promising results have been achieved in the areas of object detection and classification, few works have provided an end-to-end solution to the perception problems in the autonomous driving field. In this paper, we make two contributions. Firstly, we fully enhanced our previously released TT100K benchmark and provide 16,817 elaborately labeled Tencent Street View panoramas.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Color Reduction based on Categorical Perception
- Log in to post comments
This paper addresses the problem of color reduction which aims at computing a compact representation of a color coordinate
system. By capitalizing on studies that have suggested the existence of eleven focal colors, we conducted subjective
experiments which exploited the categorical nature of human color perception. This paper describes a novel color reduction
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION USING SVM CLASSIFICATION ON MIC-MACRO PATTERNS
- Log in to post comments
Real-time identification of facial expressions is an important topic in the area of human computer interaction and pattern recognition. The research has gained significant attention in recent years. However, many challenges still exist. This is because an individual might display different expressions at different times even for the same mood. Expressions can also be influenced by health. Our proposed framework aims to capture unique information related to facial expressions from salient patches.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views- Read more about DIRECT MULTI-SCALE DUAL-STREAM NETWORK FOR PEDESTRIAN DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views