- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation

- Read more about IMPROVING DISPARITY MAP ESTIMATION FOR MULTI-VIEW NOISY IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
A robust multi-view disparity estimation algorithm for noisy images is presented. The proposed algorithm constructs 3D focus image stacks (3DFIS) by projecting and stacking multi-view images and estimates a disparity map based on the 3DFIS. To make the algorithm robust to noise and occlusion, a texture-based view selection and patch size variation scheme based on texture map is proposed.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about ADAPTIVE VISUAL TARGET TRACKING BASED ON LABEL CONSISTENT K-SVD SPARSE CODING AND KERNEL PARTICLE FILTER
- Log in to post comments
We propose an adaptive visual target tracking algorithm based on Label-Consistent K-Singular Value Decomposition (LC-KSVD) dictionary learning. To construct target templates, local patch features are sampled from foreground and background of the target. LC-KSVD then is applied to these local patches to simultaneously estimate a set of low-dimension dictionary and classification parameters (CP). To track the target over time, a kernel particle filter (KPF) is proposed that integrates both local and global motion information of the target.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about AIRCRAFT FUSELAGE DEFECT DETECTION USING DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
To ensure flight safety of aircraft structures, it is necessary to have regular maintenance using visual and nondestructive inspection (NDI) methods. In this paper, we propose an automatic image-based aircraft defect detection using Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work for aircraft defect detection using DNNs. We perform a comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art feature descriptors and show that the best performance is achieved by vgg-f DNN as feature extractor with a linear SVM classifier.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views- Read more about GLAND SEGMENTATION GUIDED BY GLANDULAR STRUCTURES: A LEVEL SET FRAMEWORK WITH TWO LEVELS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Probabilistic Approach to People-Centric Photo Selection and Sequencing
- Log in to post comments
We present a crowdsourcing (CS) study to examine how specific attributes probabilistically affect the selection and sequencing of images from personal photo collections. 13 image attributes are explored, including 7 people-centric properties. We first propose a novel dataset shaping technique based on Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) to identify a subset of photos in which the attributes of interest are uniformly distributed and minimally correlated.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views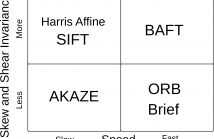
- Read more about BAFT: Binary Affine Feature Transform
- Log in to post comments
We introduce BAFT, a fast binary and quasi affine invariant local image feature. It combines the affine invariance of Harris Affine feature descriptors with the speed of binary descriptors such as BRISK and ORB. BAFT derives its speed and precision from sampling local image patches in a pattern that depends on the second moment matrix of the same image patch. This approach results in a fast but discriminative descriptor, especially for image pairs with large perspective changes.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about CAN NO-REFERENCE IMAGE QUALITY METRICS ASSESS VISIBLE WAVELENGTH IRIS SAMPLE QUALITY?
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about Audio-Visual Attention: Eye-Tracking Dataset and Analysis ToolBox
- Log in to post comments
Although many visual attention models have been proposed, very few saliency models investigated the impact of audio information. To develop audio-visual attention models, researchers need to have a ground truth of eye movements recorded while exploring complex natural scenes in different audio conditions. They also need tools to compare eye movements and gaze patterns between these different audio conditions.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 ViewsThe capability of determining the quality of target detections is important for applications using smart cameras, such as autonomous robotics and surveillance. We propose to estimate the quality of target detections by integrating the target location uncertainty over polygonal domains, which represent the fields of view of the cameras. We define a framework based on numerical integration that easily accommodates multiple models for uncertainty and fields of view.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views