
- Read more about Online Learning for Indoor Asset Detection
- Log in to post comments
Building floor plans with locations of safety, security, and energy assets such as IoT sensors, fire alarms, etc. are vital for climate control, emergency response, safety, and maintenance of building infrastructure. Existing approaches to building survey are tedious, error prone, and involve an operator with a clipboard and pen, enumerating and localizing assets in each room. We propose an interactive method for a human operator to use an app on a smartphone, which can detect, classify, and localize assets of interest, to expedite such a task.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views
- Read more about Improving Neural Non-Maximum Suppression For Object Detection By Exploiting Interest-Point Detector
- Log in to post comments
Non-maximum suppression (NMS) is a post-processing step in almost every visual object detector. Its goal is to drastically prune the number of overlapping detected candidate regions-of-interest (ROIs) and replace them with a single, more spatially accurate detection. The default algorithm (Greedy NMS) is fairly simple and suffers from drawbacks, due to its need for manual tuning. Recently, NMS has been improved using deep neural networks that learn how to solve a spatial overlap-based detections rescoring task in a supervised manner, where only ROI coordinates are exploited as input.
- Categories:
 151 Views
151 Views
- Read more about Learning Lightweight Pedestrian Detector with Hierarchical Knowledge Distillation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about 3D Facial Expression Recognition Based on Multi-View and Prior Knowledge Fusion
- Log in to post comments
MMSP2019.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about RRPN: Radar Region Proposal Network for Object Detection in Autonomous Vehicles
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views
- Read more about When Spatially-Variant Filtering Meets Low-Rank Regularization: Exploiting Non-Local Similarity for Single Image Interpolation
- Log in to post comments
This paper combines spatially-variant filtering and non-local low-rank regularization (NLR) to exploit non-local similarity in natural images in addressing the problem of image interpolation. We propose to build a carefully designed spatially-variant, non-local filtering scheme to generate a reliable estimate of the interpolated image and utilize NLR to refine the estimation. Our work uses a simple, parallelizable algorithm without the need to solve complicated optimization problems.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views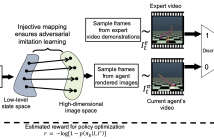
- Read more about Injective State-Image Mapping facilitates Visual Adversarial Imitation Learning
- Log in to post comments
The growing use of virtual autonomous agents in applications like games and entertainment demands better control policies for natural-looking movements and actions. Unlike the conventional approach of hard-coding motion routines, we propose a deep learning method for obtaining control policies by directly mimicking raw video demonstrations. Previous methods in this domain rely on extracting low-dimensional features from expert videos followed by a separate hand-crafted reward estimation step.
mmps_final.pdf
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about End-to-End Conditional GAN-based Architectures for Image Colourisation
- Log in to post comments
In this work recent advances in conditional adversarial networks are investigated to develop an end-to-end architecture based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to directly map realistic colours to an input greyscale image. Observing that existing colourisation methods sometimes exhibit a lack of colourfulness, this paper proposes a method to improve colourisation results. In particular, the method uses Generative Adversarial Neural Networks (GANs) and focuses on improvement of training stability to enable better generalisation in large multi-class image datasets.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
- Read more about STEADIFACE: REAL-TIME FACE-CENTRIC STABILIZATION ON MOBILE PHONES
- Log in to post comments
We present Steadiface, a new real-time face-centric video stabilization method that simultaneously removes hand shake and keeps subject's head stable. We use a CNN to estimate the face landmarks and use them to optimize a stabilized head center. We then formulate an optimization problem to find a virtual camera pose that locates the face to the stabilized head center while retains smooth rotation and translation transitions across frames. We test the proposed method on fieldtest videos and show it stabilizes both the head motion and background.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views