- Read more about Structure from sound with incomplete data
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we consider the problem of jointly localizing a microphone array and identifying the direction of arrival of acoustic events. Under the assumption that the sources are in the far field, this problem can be formulated as a constrained low-rank matrix factorization with an unknown column offset. Our focus is on handling missing entries, particularly when the measurement matrix does not contain a single complete column. This case has not received attention in the literature and is not handled by existing algorithms, however it is prevalent in practice.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views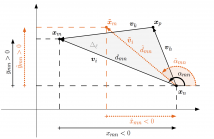
Self-localization of nodes in a sensor network is typically achieved using either range or direction measurements; in this paper, we show that a constructive combination of both improves the estimation. We propose two localization algorithms that make use of the differences between the sensors’ coordinates, or edge vectors; these can be calculated from measured distances and angles. Our first method improves the existing edge-multidimensional scaling algorithm (E-MDS) by introducing additional constraints
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Generalised Sidelobe Canceller for noise reduction in hearing devices using an external microphone
- Log in to post comments
The use of an external microphone in conjunction with an existing local microphone array can be particularly beneficial for noise reduction tasks that are critical for hearing devices, such as cochlear implants and hearing aids. Recent work has already demonstrated how an external microphone signal can be effectively incorporated into the common noise reduction technique of using a Minimum Variance Distortionless Response (MVDR) beamformer.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Speech Dereverberation based on Convex Optimization Algorithms for Group Sparse Linear Prediction
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we consider methods for improving far-field speech recognition using dereverberation based on sparse multi-channel linear prediction. In particular, we extend successful methods based on nonconvex iteratively reweighted least squares, that look for a sparse desired speech signal in the short-term Fourier transform domain, by proposing sparsity promoting convex functions. Furthermore, we show how to improve performance by applying regularization into both the reweighted least squares and convex methods.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views
- Read more about Time of Arrival Disambiguation Using the Linear Radon Transform
- Log in to post comments
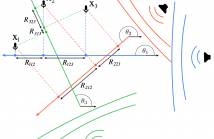
Echo labeling, the challenging task of assigning acoustic reflections to image sources, is equivalent to the highly-important disambiguation task in room geometry inference. A method using the Radon transform, an image processing tool, is proposed to address this challenge. The method relies on acoustic wavefront detection in room impulse response stacks, obtained with a uniform linear array of loudspeakers and one microphone. We show in our experiments that the proposed method can both label and detect echoes.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Microphone Array Speech Denoising Modeled by Tensor Filtering
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a novel speech denoising method based on tensor filtering, in which the microphone array speech signal is constructed by tensor data and processed by tensor filtering model. The multi-microphone signal is represented with three-order tensor space in the way of channel, time and frequency. Noise can be reduced by finding the lower-rank approximation of the three-order tensor with tucker model. MDL (Minimum Description Length) criterion is used to estimate the optimal tensor rank.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views- Read more about LCMV Beamforming with Subspace Projection for Multi-Speaker Speech Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP_D3.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views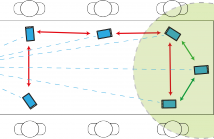
These slides were produced to complement the lecture presentation delivered at ICASSP 2016 for our paper on distributed beamforming. Please find the abstract below.
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 ViewsReverberation is well-known to have a detrimental impact on many localization methods for audio sources. We address this problem by imposing a model for the early reflections as well as a model for the audio source itself. Using these models, we propose two iterative localization methods that estimate the direction-of-arrival (DOA) of both the direct path of the audio source and the early reflections.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 ViewsPages
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4