
- Read more about A FAIR AND SCALABLE POWER CONTROL SCHEME IN MULTI-CELL MASSIVE MIMO
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Deep CNN for Wideband mmWave Massive MIMO Channel Estimation using Frequency Correlation
- Log in to post comments
For millimeter wave (mmWave) systems with large-scale arrays, hybrid processing structure is usually used at both transmitters and receivers to reduce the complexity and cost, which poses a very challenging issue in channel estimation, especially at the low transmit signal-to-noise ratio regime. In this paper, deep convolutional neural network (CNN) is employed to perform wideband channel estimation for mmWave massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views
- Read more about Secure MIMO Interference Channel with Con dential Messages and Delayed CSIT
- Log in to post comments
Slide of Presentation in ICASSP 2019
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views- Read more about On Massive MIMO Cellular Systems Resilience to Radar Interference
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we consider a massive multiple-input multiple output (MIMO) communication system using 5G New Radio compliant
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about CHANNEL ESTIMATION USING 1-BIT QUANTIZATION AND OVERSAMPLING FOR LARGE-SCALE MULTIPLE-ANTENNA SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Large-scale multiple-antenna systems have been identified as a promising technology for the next generation of wireless systems. However, by scaling up the number of receive antennas the energy consumption will also increase. One possible solution is to use low-resolution analog-to-digital converters at the receiver. This paper considers large-scale multiple-antenna uplink systems with 1-bit analog-to-digital converters on each receive antenna.
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Complementary sequence encoding for 1D and 2D constant-modulus OFDM transmission at millimeter wave frequencies
- Log in to post comments
This paper develops a method for constructing an OFDM signal from a pair of complementary sequences so that the resulting signal is constant-modulus. A recursive method of constructing complementary sequences is developed such that the length of the signal grows linearly with the number of information symbols encoded. The constant-modulus property is exploited at each stage of the backwards symbol-decoding iteration through simple means to progressively reduce noise.
ICASSPposter.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views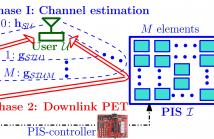
- Read more about Channel Estimation and Low-complexity Beamforming Design for Passive Intelligent Surface Assisted MISO Wireless Energy Transfer
- Log in to post comments
Usage of passive intelligent surface (PIS) is emerging as a low-cost green alternative to massive antenna systems for realizing high energy beamforming (EB) gains. To maximize its realistic utility, we present a novel channel estimation (CE) protocol for PIS-assisted energy transfer (PET) from a multiantenna power beacon (PB) to a single-antenna energy harvesting (EH) user. Noting the practical limitations of PIS and EH user, all computations are carried out at PB having required active components and radio resources.
- Categories:
 133 Views
133 Views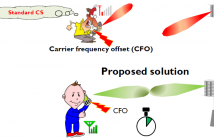
- Read more about [Poster] Localized Random Sampling for Robust Compressive Beam Alignment
- Log in to post comments
Compressed sensing (CS)-based beam alignment is a promising solution for rapid link configuration in millimeter wave (mmWave)
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views
- Read more about MASSIVE MIMO CHANNEL ESTIMATION FOR MILLIMETER WAVE SYSTEMS VIA MATRIX COMPLETION
- Log in to post comments
Millimeter wave (mmWave) massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) systems realizing directive beamforming require reliable estimation of the wireless propagation channel. However, mmWave channels are characterized by high variability that severely challenges their recovery over short training periods. Current channel estimation techniques exploit either the channel sparsity in the beamspace domain or its low-rank property in the antenna domain, nevertheless, they still require large numbers of training symbols for the satisfactory performance.
- Categories:
 204 Views
204 Views