
The IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP) is a flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society. GlobalSIP'15 will be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, December 14-16, 2015. The conference will focus on signal and information processing with an emphasis on up-and-coming signal processing themes. The conference will feature world-class speakers, tutorials, exhibits, and sessions consisting of poster or oral presentations. Outstanding papers will be selected for Best Paper Awards or Best Student Paper Awards; a paper is eligible for a best student paper award if the first author of the paper is a student. IEEE Signal Processing Society and National Science Foundation will provide travel grants to eligible students.

- Read more about Optimal Pricing for Interference Control in Time-reversal Device-to-Device Uplinks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views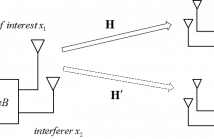
- Read more about Likelihood-Based Modulation Classification for MU-MIMO Systems
- Log in to post comments
The problem of optimal likelihood based modulation classification (MC) for optimal detection in 2x2 multiuser MIMO (MU-MIMO) receivers is considered. The optimal Log-MAP classifier is computationally exhaustive, and its sub-optimal Max-Log-MAP version poses remarkable degradation in performance. Between these two extremes, we propose four computationally simplified methods for MC, by taking special subsets of Euclidean distance computations that constitute the decision metric.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views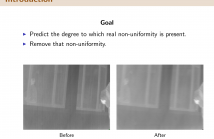
- Read more about Non-uniformity Correction of IR Images using Natural Scene Statistics
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views- Read more about Key frames hysteresis-seeking based on motion change points for RGB-D video
- Log in to post comments
Key-frame extraction has been a focused problem of human action recognition due to its effectiveness, efficiency and importance in action understanding. According to the characteristics of human motion perception, this paper proposes a new key-frame extraction framework based on motion change points. And in order to detect motion change points robustly, a hysteresis extrema seeking algorithm has been developed. Experimental results have demonstrated the good performance of the proposed methods.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about DQM: Decentralized Quadratically Approximated Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Low-Complexity MIMO Detector with 1024-QAM
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, dual layer multiple-input multiple-output (2x2 MIMO) systems that use the 1024-QAM modulation are studied. We build on the layered orthogonal lattice detector (LORD), which achieves optimal maximum-likelihood (ML) performance, but which has high complexity with 1024-QAM, and argue that the low-complexity version of LORD (LC-LORD) introduces a significant performance degradation, especially with high channel correlation. We propose several approaches that outperform LC-LORD at a lower complexity.
- Categories:
 111 Views
111 Views- Read more about DoA Estimation and Capacity Analysis for 3D Massive-MIMO/FD-MIMO OFDM System
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Brain Functional Connectivity Analysis Using Mutual Information
- Log in to post comments
presentation.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about MPDQ-Based High-Order QAM Detection Scheme for Massive MIMO with Low-Precision Quantization
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Binary Rate Distortion With Side Information: The Asymmetric Correlation Channel Case
- Log in to post comments
Advancing over up-to-date information theoretic results that assume symmetric correlation models, in this work we consider the problem of lossy binary source coding with side information, where the correlation is expressed by a generic binary asymmetric channel. Specifically, we present an in-depth analysis of rate distortion with side information available to both the encoder and decoder (conventional predictive), as well as the Wyner-Ziv problem for this particular setup.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views