
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about IMAGE REPRESENTATION USING SUPERVISED AND UNSUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS ON COMPLEX DOMAIN
- Log in to post comments
Matrix factorization (MF) and its extensions have been intensively studied in computer vision and machine learning. In this paper, unsupervised and supervised learning methods based on MF technique on complex domain are introduced. Projective complex matrix factorization (PCMF) and discriminant projective complex matrix factorization (DPCMF) present two frameworks of projecting complex data to a lower dimension space. The optimization problems are formulated as the minimization of the real-valued functions of complex variables.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about LOCALITY-PRESERVING COMPLEX-VALUED GAUSSIAN PROCESS LATENT VARIABLE MODEL FOR ROBUST FACE RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views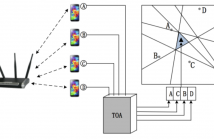
- Read more about ROBUST SEQUENCE-BASED LOCALIZATION IN ACOUSTIC SENSOR NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Acoustic source localization in sensor network is a challenging task because of severe constraints on cost, energy, and effective range of sensor devices. To overcome these limitations in existing solutions, this paper formally describes, designs, implements, and evaluates a Half Plane Intersection method to Sequence-Based Localization, i.e., HPI-SBL, in distributed smartphone networks. The localization space can be divided into distinct regions, and each region can be uniquely identified by the node sequence that represents the ranking of distances from the reference nodes to the region.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about COMPLEX-VALUED GAUSSIAN PROCESS LATENT VARIABLE MODEL FOR PHASE-INCORPORATING SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about MODAL DECOMPOSITION OF MUSICAL INSTRUMENT SOUND VIA ALTERNATING DIRECTION METHOD OF MULTIPLIERS
- Log in to post comments
For a musical instrument sound containing partials, or modes, the behavior of modes around the attack time is particularly important. However, accurately decomposing it around the attack time is not an easy task, especially when the onset is sharp. This is because spectra of the modes are peaky while the sharp onsets need a broad one. In this paper, an optimization-based method of modal decomposition is proposed to achieve accurate decomposition around the attack time.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about COMPLEX-VALUED GAUSSIAN PROCESS LATENT VARIABLE MODEL FOR PHASE-INCORPORATING SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Continuous Security In IoT Using Blockchain
- Log in to post comments
The two major roadblocks for state of the art Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure like smart buildings, smart cities, etc. are lack of trust between various entities of system and single point of failure which is a vulnerability causing extreme damage to the whole system. This paper proposes a blockchain based IoT security solution where, trust is established through the immutable and decentralized nature of blockchain. The distributed nature of blockchain makes the system more robust and immune to single point of failure.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views
- Read more about A Supervised STDP-Based Training Algorithm for Living Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
Neural networks have shown great potential in many applications like speech recognition, drug discovery, image classification, and object detection. Neural network models are inspired by biological neural networks, but they are optimized to perform machine learning tasks on digital computers.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Combining MatrixOn the SNR Variability in Noisy Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Compressed sensing (CS) is a sampling paradigm
that allows to simultaneously measure and compress signals that
are sparse or compressible in some domain. The choice of a
sensing matrix that carries out the measurement has a defining
impact on the system performance and it is often advocated to
draw its elements randomly. It has been noted that in the presence
of input (signal) noise, the application of the sensing matrix causes
SNR degradation due to the noise folding effect. In fact, it might
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views