- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation

- Read more about SHOW, TRANSLATE AND TELL
- Log in to post comments
Humans have an incredible ability to process and understand
information from multiple sources such as images,
video, text, and speech. Recent success of deep neural
networks has enabled us to develop algorithms which give
machines the ability to understand and interpret this information.
There is a need to both broaden their applicability and
develop methods which correlate visual information along
with semantic content. We propose a unified model which
jointly trains on images and captions, and learns to generate
STT_v5.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views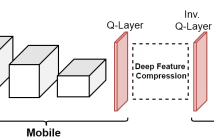
- Read more about MULTI-TASK LEARNING WITH COMPRESSIBLE FEATURES FOR COLLABORATIVE INTELLIGENCE
- Log in to post comments
A promising way to deploy Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based services on mobile devices is to run a part of the AI model (a deep neural network) on the mobile itself, and the rest in the cloud. This is sometimes referred to as collaborative intelligence. In this framework, intermediate features from the deep network need to be transmitted to the cloud for further processing. We study the case where such features are used for multiple purposes in the cloud (multi-tasking) and where they need to be compressible in order to allow efficient transmission to the cloud.
ICIP_2019.pptx
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about DEEP UNSUPERVISED LEARNING FOR SIMULTANEOUS VISUAL ODOMETRY AND DEPTH ESTIMATION
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about IMPRESSION ESTIMATION FOR DEFORMED PORTRAITS WITH A LANDMARK-BASED RANKING NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, it has become a trend for people to manipulate their own portraits before posting them on a social networking service. However, it is difficult to get a desired portrait after manipulation without sufficient experience or skill. To obtain a simpler and more effective portrait manipulation technique, we consider an automated portrait manipulation method based on five impression words: clear, sweet, elegant, modern, and dynamic.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about MULTIMODAL LATENT FACTOR MODEL WITH LANGUAGE CONSTRAINT FOR PREDICATE DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
poster-2.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Multimodal Point Distribution Model for Anthropological Landmark Detection
- Log in to post comments
While current landmark detection algorithms offer a good approximation of the landmark locations, they are often unsuitable for the use in biological research. We present multimodal landmark detection approach, based on Point distribution model that detects a larger number of anthropologically relevant landmarks than the current landmark detection algorithms.
At the same time we show that improving detection accuracy of initial vertices, using image information, to which
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about VISUAL LOCALIZATION USING SPARSE SEMANTIC 3D MAP
- Log in to post comments
Accurate and robust visual localization under a wide range of viewing condition variations including season and illumination changes, as well as weather and day-night variations, is the key component for many computer vision and robotics applications. Under these conditions, most traditional methods would fail to locate the camera. In this paper we present a visual localization algorithm that combines structure-based method and image-based method with semantic information.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about RESIDUAL DILATION BASED FEATURE PYRAMID NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about IMPROVED FOURIER MELLIN INVARIANT FOR ROBUST ROTATION ESTIMATION WITH OMNI-CAMERAS
- Log in to post comments
Spectral methods such as the improved Fourier Mellin Invariant (iFMI) transform have proved to be faster, more robust
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views