- Image/Video Storage, Retrieval
- Image/Video Processing
- Image/Video Coding
- Image Scanning, Display, and Printing
- Image Formation

- Read more about MOTION SALIENCY BASED GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORK FOR UNDERWATER MOVING OBJECT SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
The underwater moving object segmentation is a challenging task. The problems like absorbing, scattering and attenuation of light rays between the scene and the imaging platform degrades the visibility of image or video frames. Also, the back-scattering of light rays further increases the problem of underwater video analysis, because the light rays interact with underwater particles and scattered back to the sensor. In this paper, a novel Motion Saliency Based Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) for Underwater Moving Object Segmentation (MOS) is proposed.
Poster.pdf
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Single Image Depth Estimation Using Deep Adversarial Training
- Log in to post comments
Scene understanding is an active area of research in computer vision that encompasses several different problems. The LiDARs and stereo depth sensor have their own restrictions such as light sensitiveness, power consumption and short-range. In this paper, we propose a two-stream deep adversarial network for single image depth estimation in RGB images. For stream I network, we propose a novel encoder-decoder architecture using residual concepts to extract course-level depth features.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about Fashion Recommendation on Street Images
- Log in to post comments
Learning the compatibility relationship is of vital importance to a fashion recommendation system, while existing works achieve this merely on product images but not on street images in the complex daily life scenario. In this paper, we propose a novel fashion recommendation system: Given a query item of interest in the street scenario, the system can return the compatible items. More specifically, a two-stage curriculum learning scheme is developed to transfer the semantics from the product to street outfit images.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views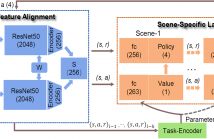
- Read more about MEMORY-BASED PARAMETERIZED SKILLS LEARNING FOR MAPLESS VISUAL NAVIGATION
- Log in to post comments
The recently-proposed reinforcement learning for mapless visual navigation can generate an optimal policy for searching different targets. However, most state-of-the-art deep reinforcement learning (DRL) models depend on hard rewards to learn the optimal policy, which can lead to the lack of previous diverse experiences. Moreover, these pre-trained DRL models cannot generalize well to un-trained tasks. To overcome these problems above, in this paper, we propose a Memorybased Parameterized Skills Learning (MPSL) model for mapless visual navigation.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views
- Read more about COMPRESSIVE SENSING RECONSTRUCTION BASED ON STANDARDIZED GROUP SPARSE REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Non-local sparsity has been widely concerned in image compressive
sensing. Considering the difference of distribution
characteristic of among group-based sparse coefficients of
image, a new method for image compressive sensing reconstruction
(ICSR) is proposed based on the z-scores standardized
group sparse representation (ZSGSR). Here, the
similar patch groups of the image are firstly extracted and
decomposed by adaptive PCA dictionary, then the resulting
coefficients are normalized using z-score standardization in
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about Denoising Adversarial Networks for Rain Removal and Reflection Removal
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
poster1192.pdf
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about CLUSTERING IMAGES BY UNMASKING - A NEW BASELINE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about EARLY WILDFIRE SMOKE DETECTION BASED ON MOTION-BASED GEOMETRIC IMAGE TRANSFORMATION AND DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Immediate and accurate detection of wildfire is essentially important in forest monitoring systems
•One of the most harmful hazards in rural areas
•For wildfire detection, the use of visible-range video captured by surveillance cameras are suitable
•They can be deployed and operated in a cost-effective manner
•The challenge is to provide a robust detection system with negligible false positive rates
•If the flames are visible, they can be detected by analyzing the motion and color clues of a video
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about Blind Quality Assessment for 3D-Synthesized Images by Measuring Geometric Distortions and Image Complexity
- Log in to post comments
Free viewpoint video (FVV), owing to its comprehensive applications in immersive entertainment, remote surveillance and distanced education, has received extensive attention and been regarded as a new important direction of video technology development. Depth image-based rendering (DIBR) technologies are employed to synthesize FVV images in the “blind” environment. Therefore, a real-time reliable blind quality assessment metric is urgently required. However, existing stste-of-art quality assessment methods are limited to estimate geometric distortions generated by DIBR.
icassp-2019.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Learning Motion Disfluencies for Automatic Sign Language Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a novel technique for the automatic detection of word boundaries within continuous sentence expressions in Japanese Sign Language from three-dimensional body joint positions. First, the flow of signed sentence data within a temporal neighborhood is determined utilizing the spatial correlations between line segments of inter-joint pairs. Next, a frame-wise binary random forest classifier is trained to distinguish word and non-word frame content based on the extracted spatio-temporal features.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views