
Detection of cell nuclei in microscopic images is a challenging research topic, because of limitations in cellular image quality and diversity of nuclear morphology, i.e. varying nuclei shapes, sizes, and overlaps between multiple cell nuclei. This has been a topic of enduring interest with promising recent success shown by deep learning methods. These methods train for example convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with a training set of input images and known, labeled nuclei locations. Many of these methods are supplemented by spatial or morphological processing.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about DEEP MR BRAIN IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION USING STRUCTURAL PRIORS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about MULTICLASS WEIGHTED LOSS FOR INSTANCE SEGMENTATION OF CLUTTERED CELLS
- Log in to post comments
We propose a new multiclass weighted loss function for instance segmentation of cluttered cells. We are primarily motivated by the need of developmental biologists to quantify and model the behavior of blood T-cells which might help us in understanding their regulation mechanisms and ultimately help researchers in their quest for developing an effective immunotherapy cancer treatment.
postericip.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views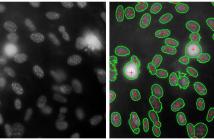
- Read more about CELL SEGMENTATION VIA REGION-BASED ELLIPSE FITTING
- Log in to post comments
We present a region based method for segmenting and splitting
images of cells in an automatic and unsupervised manner.
The detection of cell nuclei is based on the Bradley’s method.
False positives are automatically identified and rejected based
on shape and intensity features. Additionally, the proposed
method is able to automatically detect and split touching cells.
To do so, we employ a variant of a region based multi-ellipse
fitting method (DEFA) that makes use of constraints on the
- Categories:
 87 Views
87 Views
- Read more about LOW COMPLEXITY CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK FOR VESSEL SEGMENTATION IN PORTABLE RETINAL DIAGNOSTIC DEVICES
- Log in to post comments
Retinal vessel information is helpful in retinal disease screening and diagnosis. Retinal vessel segmentation provides useful information about vessels and can be used by physicians during intraocular surgery and retinal diagnostic operations. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are powerful tools for classification and segmentation of medical images. However, complexity of CNNs makes it difficult to implement them in portable devices such as binocular indirect ophthalmoscopes. In this paper a simplification approach is proposed for CNNs based on combination of quantization and pruning.
Poster-Retina.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about ADAPTIVE SPECULAR REFLECTION DETECTION AND INPAINTING IN COLONOSCOPY VIDEO FRAMES
- Log in to post comments
Colonoscopy video frames might be contaminated by bright spots with unsaturated values known as specular reflection. Detection and removal of such reflections could enhance the quality of colonoscopy images and facilitate diagnosis procedure. In this paper, we propose a novel two-phase method for this purpose, consisting of detection and removal phases. In the detection phase, we employ both HSV and RGB color space information for segmentation of specular reflections.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about LIVER SEGMENTATION IN CT IMAGES USING THREE DIMENSIONAL TO TWO DIMENSIONAL FULLY CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
The need for CT scan analysis is growing for diagnosis and therapy of abdominal organs. Automatic organ segmentation of abdominal CT scan can help radiologists analyze the scans faster, and diagnose disease and injury more accurately. However, existing methods are not efficient enough to perform the segmentation process for victims of accidents and emergency situations. In this paper, we propose an efficient liver segmentation with our 3D to 2D fully convolution network (3D-2D-FCN). The segmented mask is enhanced using the conditional random field on the organ’s border.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about AUTOMATIC 3-D SKELETON-BASED SEGMENTATION OF LIVER VESSELS FROM MRI AND CT FOR COUINAUD REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about Multimodal Image Registration through Simultaneous Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Multimodal image registration facilitates the combination of complementary information from images acquired with different modalities. Most existing methods require computation of the joint histogram of the images, while some perform joint segmentation and registration in alternate iterations. In this work, we introduce a new non-information-theoretical method for pairwise multimodal image registration, in which the error of segmentation – using both images – is considered as the registration cost function.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about MOSAICING OF IMAGES WITH FEW TEXTURES AND STRONG ILLUMINATION CHANGES: APPLICATION TO GASTROSCOPIC SCENES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views