
- Read more about A MULTI-SCALED RECEPTIVE FIELD LEARNING APPROACH FOR MEDICAL IMAGE SEGMENTATION
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Biomedical image segmentation has been widely studied, and lots of methods have been proposed. Among these methods, attention U-Net has achieved a promising performance. However, it has drawbacks of extracting the multi-scaled receptive field features at the high-level feature maps, resulting in the degeneration when dealing with the lesions with apparent scale variations. To solve this problem, this paper integrates an atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module in the contracting path of attention U-Net.
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views
- Read more about Lightweight V-Net for Liver Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
The V-Net based 3D fully convolutional neural networks have been widely used in liver volumetric data segmentation. However, due to the large number of parameters of these networks, 3D FCNs suffer from high computational cost and GPU memory usage. To address these issues, we design a lightweight V-Net (LV-Net) for liver segmentation in this paper. The proposed network makes two contributions. The first is that we design an inverted residual bottleneck block (IRB block) and a 3D average pooling block and apply them to the proposed LV-Net.
- Categories:
 170 Views
170 Views
- Read more about Deep Learning Based Mass Detection in Mammograms
- Log in to post comments
Mammogram is the primary imaging technique for breast cancer screening, the leading type of cancer in women worldwide. While the clinical effectiveness of mammogram has been well demonstrated, the mammographic characteristics of breast masses are quite complex. As a result, radiologists certified for reading mammography are lacking, which limits the accessibility of mammography for more population. In this paper, we propose a Computer Aided Detection (CADe) method to automatically detect masses in mammography.
- Categories:
 128 Views
128 Views
- Read more about A Multimodal Dense U-Net for Accelerating Multiple Sclerosis MRI
- Log in to post comments
The clinical analysis of magnetic resonance (MR) can be accelerated through the undersampling in the k-space (Fourier domain). Deep learning techniques have been recently received considerable interest for accelerating MR imaging (MRI). In this paper, a deep learning method for accelerating MRI is presented, which is able to reconstruct undersampled MR images obtained by reducing the k-space data in the direction of the phase encoding.
MLSP2019_poster_v4.pdf
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 Views
- Read more about Multi-Label Classification for Automatic Human Blastocyst Grading with Severely Imbalanced Data
- Log in to post comments
Quality scores assigned to blastocyst inner cell mass (ICM), trophectoderm (TE), and zona pellucida (ZP) are critical markers for predicting implantation potential of a human blastocyst in IVF treatment. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown success in various image classification tasks, including classification of blastocysts into two quality categories. However, the problem of multi-label multi-class classification for blastocyst grading remains unsolved.
- Categories:
 92 Views
92 Views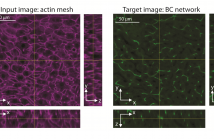
- Read more about PREDICTION OF MULTIPLE 3D TISSUE STRUCTURES BASED ON SINGLE-MARKER IMAGES USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
A quantitative understanding of complex biological systems such as tissues requires reconstructing the structure of the different components of the system. Fluorescence microscopy provides the means to visualize simultaneously several tissue components. However, it can be time consuming and is limited by the number of fluorescent markers that can be used. In this study, we describe a toolbox of algorithms based on convolutional neural networks for the prediction of 3D tissue structures by learning features embedded within single-marker images.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about BiRA-Net: Bilinear Attention Net for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading
- Log in to post comments
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a common retinal disease that leads to blindness. For diagnosis purposes, DR image grading aims to provide automatic DR grade classification, which is not addressed in conventional research methods of binary DR image classification. Small objects in the eye images, like lesions and microaneurysms, are essential to DR grading in medical imaging, but they could easily be influenced by other objects.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Read more about DEEP U-NET REGRESSION AND HAND-CRAFTED FEATURE FUSION FOR ACCURATE BLOOD VESSEL SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Automated curvilinear image segmentation is a crucial step to characterize and quantify the morphology of blood vessels across scale. We propose a dual pipeline RF_OFB+U-NET that fuses U-Net deep learning features with a low level image feature filter bank using the random forests classifier for vessel segmentation. We modify the U-Net CNN architecture to provide a foreground vessel regression likelihood map that is used to segment both arteriole and venule blood vessels in mice dura mater tissues.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
- Read more about A dual attention dilated residual network for liver lesion classification and localization on CT images
- Log in to post comments
Automatic liver lesion classification on computed
tomography images is of great importance to early cancer
diagnosis and remains a challenging task. State-of-the-art
liver lesion classification algorithms are currently based on
manually selected regions of interest (ROIs) or automatically
detected ROIs. However, liver lesions usually vary in size
and shape, which makes the ROI selection process laborintensive
and also poses an obstacle to automatic lesion
detection. In this paper, we propose a dual-attention dilated
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views