
- Read more about UNMIXING DYNAMIC PET IMAGES: COMBINING SPATIAL HETEROGENEITY AND NON-GAUSSIAN NOISE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Semi-Supervised Transfer Learning for Convolutional Neural Networks for Glaucoma Detection
- Log in to post comments
Convolutional neural network (CNN) can be applied in glaucoma detection for achieving good performance.
However, its performance depends on the availability of a large number of the labelled samples for its training phase.
To solve this problem, this paper present a semi-supervised transfer learning CNN model for automatic glaucoma detection based on both labeled and unlabeled data.
First, a pre-trained CNN from non-medical data is fine-tuned and trained in a supervised fashion using the labeled data.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views
- Read more about AN EVENT-CONTRASTIVE CONNECTOME NETWORK FOR AUTOMATIC ASSESSMENT OF INDIVIDUAL FACE PROCESSING AND MEMORY ABILITY
- Log in to post comments
Human adapt their behaviors by continuously monitoring one another to function socially in our society. The ability to process face identity from memory is a crucial basic capability. In this work, we propose an event-contrastive connectome network (E-cCN) in representing brain’s functional connectivity with novel contrastive loss to handle layers of fMRI data variabilities exists under different controlled stimuli events to achieve improved automatic assessing of an individual’s face processing and memory ability.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about SKIN LESION CLASSIFICATION USING HYBRID DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Skin cancer is one of the major types of cancers with an increasing incidence over the past decades. Accurately diagnosing skin lesions to discriminate between benign and malignant skin lesions is crucial to ensure appropriate patient treatment. While there are many computerised methods for skin lesion classification, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been shown to be superior over classical methods.
- Categories:
 121 Views
121 Views
- Read more about POLARITY INVARIANT TRANSFORMATION FOR EEG MICROSTATES ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
Electroencephalography (EEG) has been widely used in human brain research. Several techniques in EEG relies on analyzing the topographical distribution of the data. One of the most common analysis is EEG microstate (EEG-ms). EEG-ms reflects the stable topographical representation of EEG signal lasting a few dozen milliseconds. EEG-ms were associated with resting state fMRI networks and were associated with mental processes and abnormalities.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views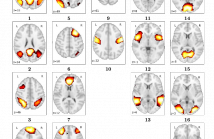
- Read more about HOW MANY FMRI SCANS ARE NECESSARY AND SUFFICIENT FOR RESTING BRAIN CONNECTIVITY ANALYSIS?
- Log in to post comments
Functional connectivity analysis by detecting neuronal coactivation in the brain can be efficiently done using Resting State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (rs-fMRI) analysis. Most of the existing research in this area employ correlation-based group averaging strategies of spatial smoothing and temporal normalization of fMRI scans, whose reliability of results heavily depends on the voxel resolution of fMRI scan as well as scanning duration. Scanning period from 5 to 11 minutes has been chosen by most of the studies while estimating the connectivity of brain networks.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about SEGMENTATION OF LUNG TUMOR IN CONE BEAM CT IMAGES BASED ON LEVEL-SETS
- Log in to post comments
poster_v2.pdf
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views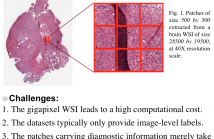
- Read more about WHOLE SLIDE IMAGE CLASSIFICATION VIA ITERATIVE PATCH LABELLING
- Log in to post comments
Brain tumor can be a fatal disease in the world. With the aim of improving survival rates, many computerized algorithms have been proposed to assist the pathologists to make a diagnosis, using Whole Slide Pathology Images (WSI). Most methods focus on performing patch-level classification and aggregating the patch-level results to obtain the image classification. Since not all patches carry diagnostic information, it is thus important for our algorithm to recognize discriminative and non-discriminative patches.
- Categories:
 184 Views
184 Views
- Read more about 3D Multi-Scale Convolutional Networks For Glioma Grading using MR Images
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 ViewsNumerous recent papers have demonstrated the utility of graph theoretical analysis in conjunction with sparse inverse covariance estimation (SICE) in understanding the modulation of brain connectivity associated with neuropathology. These concepts may complement established knowledge of functional covariance obtained using principal component analysis (PCA) that can reduce whole data representations of brain data to essential disease specific patterns.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views