- Communication and Sensing aspects of Sensor Networks, Wireless and Ad-Hoc Networks
- Communication Systems and Applications
- MIMO Communications and Signal Processing
- Signal Transmission and Reception

- Read more about A New Perspective on Randomized Gossip Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
In this short note we propose a new approach for the design and analysis of randomized gossip algorithms which can be used to solve the average consensus problem. We show how the Randomized Block Kaczmarz (RBK) method—a method for solving linear systems—works as gossip algorithm when applied to a special system encoding the underlying network. The famous pairwise gossip algorithm arises as a special case.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about A New Perspective on Randomized Gossip Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
In this short note we propose a new approach for the design and analysis of randomized gossip algorithms which can be used to solve the average consensus problem. We show how the Randomized Block Kaczmarz (RBK) method—a method for solving linear systems—works as gossip algorithm when applied to a special system encoding the underlying network. The famous pairwise gossip algorithm arises as a special case.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about A New Perspective on Randomized Gossip Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
In this short note we propose a new approach for the design and analysis of randomized gossip algorithms which can be used to solve the average consensus problem. We show how the Randomized Block Kaczmarz (RBK) method—a method for solving linear systems—works as gossip algorithm when applied to a special system encoding the underlying network. The famous pairwise gossip algorithm arises as a special case.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views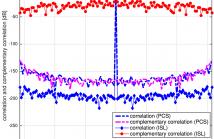
- Read more about Construction of Complementary Sets of Sequences with Low Aperiodic Correlation and Complementary Correlation
- Log in to post comments
The construction of complementary sets of unimodular sequences of length N, with low correlation and complementary correlation coefficients is addressed. The design criterion is based on the minimisation of a cost function that penalizes the integrated side lobe as well as the sum of the complementary correlations of the sequences in the set. Numerical solution to the proposed cost function is obtained using conventional optimization methods.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about IEEE SP Cup 2016 Report - Team MGLS
- Log in to post comments
Extracting the Electric Network Frequency (ENF) fluctuations from an audio recording and comparing it to a reference database is a new approach in performing forensic digital audio authentication. The problem statement of the IEEE SP cup 2016 competition relates to time-varying location-dependent signature of power grids as it becomes intrinsically captured in media recordings, due to direct or indirect influences from the respective power grid. In this project signal processing and information security/forensics are collectively elaborated.
- Categories:
 184 Views
184 Views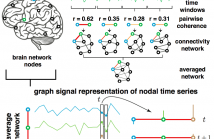
- Read more about Graph Frequency Analysis of Brain Signals
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents methods to analyze functional brain networks and signals from graph spectral perspectives. The notion of frequency and filters traditionally defined for signals supported on regular domains such as discrete time and image grids has been recently generalized to irregular graph domains, and defines brain graph frequencies associated with different levels of spatial smoothness across the brain regions. Brain network frequency also enables the decomposition of brain signals into pieces corresponding to smooth or rapid variations.
- Categories:
 131 Views
131 ViewsIn this work, a directional modulation-based technique is devised to enhance the security of a multi-antenna wireless communication system employing M-PSK modulation to convey information. The directional modulation method operates by steering the array beam in such a way that the phase of the received signal at the receiver matches that of the intended M-PSK symbol. Due to the difference between the channels of the legitimate receiver and the eavesdropper, the signals received by the eavesdropper generally encompass a phase component different than the actual symbols.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Subspace-based Adaptive Widely Linear Blind Channel Estimation for Constrained Minimum Variance CDMA Receiver
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about ENERGY DETECTION IN ISI CHANNELS USING LARGE-SCALE RECEIVER ARRAYS_PRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views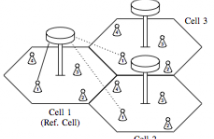
- Read more about Group-Blind Detection with Very Large Antenna Arrays in the Presence of Pilot Contamination
- Log in to post comments
Massive MIMO is, in general, severely affected by pilot contamination. As opposed to traditional detectors, we propose a group-blind detector that takes into account the presence of pilot contamination. While sticking to the traditional structure of the training phase, where orthogonal pilot sequences are reused, we use the excess antennas at each base station to partially remove interference during the uplink data transmission phase. We analytically derive the asymptotic SINR achievable with group-blind detection, and confirm our findings by simulations.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views