
- Read more about Radar Clutter Classification Using Expectation-Maximization Method
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, the problem of classifying radar clutter returns into statistically homogeneous subsets is addressed. To this end, latent variables, which represent the classes to which the tested range cells belong, in conjunction with the expectation-maximization method are jointly exploited to devise the classification architecture. Moreover, two different models for the structure of the clutter covariance matrix are considered.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Resolution Limits of 20 Questions Search Strategies for Moving Targets
- Log in to post comments
We establish fundamental limits of tracking a moving target over the unit cube under the framework of 20 questions with measurement-dependent noise. In this problem, there is an oracle who knows the instantaneous location of a target. Our task is to query the oracle as few times as possible to accurately estimate the trajectory of the moving target, whose initial location and velocity is unknown. We study the case where the oracle's answer to each query is corrupted by random noise with query-dependent discrete distribution.
poster_moving2.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about DETECTION OF SHIP WAKES IN SAR IMAGERY USING CAUCHY REGULARISATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views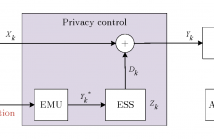
- Read more about On design of optimal smart meter privacy control strategy against adversarial MAP detection
- Log in to post comments
We study the optimal control problem of the maximum a posteriori (MAP) state sequence detection of an adversary using smart meter data. The privacy leakage is measured using the Bayesian risk and the privacy-enhancing control is achieved in real-time using an energy storage system. The control strategy is designed to minimize the expected performance of a non-causal adversary at each time instant. With a discrete-state Markov model, we study two detection problems: when the adversary is unaware or aware of the control.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about ICASSP 2020
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of detection, in the frequency domain, of a M-dimensional time series modeled as the output of a M × K MIMO filter driven by a K-dimensional Gaussian white noise, and disturbed by an additive M-dimensional Gaussian col- ored noise. We consider the study of test statistics based of the Spectral Coherence Matrix (SCM) obtained as renormalization of the smoothed periodogram matrix of the observed time series over N samples, and with smoothing span B.
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Entropy Coders Based on the Splitting of Lexicographic Intervals
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about Estimating Structural Missing Values via Low-tubal-rank Tensor Completion
- Log in to post comments
The recently proposed Tensor Nuclear Norm (TNN) minimization has been widely used for tensor completion. However, previous works didn’t consider the structural difference between the observed data and missing data, which widely exists in many applications. In this paper, we propose to incorporate a constraint item on the missing values into low-tubal-rank tensor completion to promote the structural hypothesis
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about Particle Filtering on the Complex Stiefel Manifold with Application to Subspace Tracking
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we extend previous particle filtering methods whose states were constrained to the (real) Stiefel manifold to the complex case. The method is then applied to a Bayesian formulation of the subspace tracking problem. To implement the proposed particle filter, we modify a previous MCMC algorithm so as to simulate from densities defined on the complex manifold. Also, to compute subspace estimates from particle approximations, we extend existing averaging methods to complex Grassmannians.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 130 Views
130 Views
- Read more about On the Robustness of Causal Discovery with Additive Noise Models on Discrete Data
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views