
The IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP) is a flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society. GlobalSIP'15 will be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, December 14-16, 2015. The conference will focus on signal and information processing with an emphasis on up-and-coming signal processing themes. The conference will feature world-class speakers, tutorials, exhibits, and sessions consisting of poster or oral presentations. Outstanding papers will be selected for Best Paper Awards or Best Student Paper Awards; a paper is eligible for a best student paper award if the first author of the paper is a student. IEEE Signal Processing Society and National Science Foundation will provide travel grants to eligible students.

- Read more about Optimal Wireless Power Transfer and Harvested Power Allocation for Diffusion LMS in Wireless Sensor Networks
- Log in to post comments
This paper investigates the use of wireless power transfer (WPT) for {measurement sensing} and information transmission in a wireless sensor network (WSN) performing distributed parameter estimation using an adaptive diffusion least mean-squares (LMS) strategy. We consider a hybrid WSN consisting of common sensor nodes (CNs) and super sensor nodes (SNs) that are capable of WPT. In each diffusion iteration, all nodes sense measurements and exchange parameter estimates with their neighbors. Each SN also transfers wireless power to its neighboring CNs via beamforming.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Unsupervised Keyword Spotting using Bounded Generalized Gaussian Mixture Model with ICA
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, bounded generalized Gaussian mixture model (BGGMM) using independent component analysis (ICA) is proposed and applied to an existing unsupervised keyword spotting setting for the generation of posteriorgrams. The ICA mixture model is trained without any transcription information to generate the posteriorgrams which further labels the speech frames of the keyword example(s) and test data.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 ViewsThis paper considers the detection of possible deviation from a nominal distribution for continuously valued random variables. Specifically, under the null hypothesis, samples are distributed approximately according to a nominal distribution. Any significant departure from this nominal distribution constitutes the alternative hypothesis. It is established that for such deviation detection where the nominal distribution is only specified under the null hypothesis, Kullback-Leibler distance is not a suitable measure for deviation.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Inference of Sparse Gene Regulatory Network from RNA-Seq Time Series Data
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views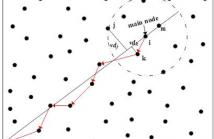
- Read more about A Small World Model for Improving Robustness of Heterogeneous Networks
- Log in to post comments
Robustness is an important and challenging issue in internet of things (IoT), where contains multiple types of heterogeneous networks. To solve this problem, we design and realize a greedy model with small world properties (GMSW) for heterogeneous sensor network of IoT. In GMSW, two greedy criteria are presented firstly, which are used to distinguish importance of different network nodes. On the basis, we define the concept of local importance of node and design a shortcut-added strategy, by which way prompts the network present small world phenomenon.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about Full waveform microseismic inversion using differential evolution algorithm
- Log in to post comments
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about A Riemannian Approach for Computing Geodesic in Elastic Shape Analysis
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views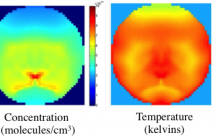
- Read more about Gaussian Mixture Prior Models for Imaging of Flow Cross Sections from Sparse Hyperspectral Measurements
- Log in to post comments
This is an overview presentation about developing accurate prior models that can capture non-Gaussian characteristics of images. The slides use tunable diode laser absorption tomography (TDLAT) as an application to show the results.
For more information, please check out the publication at IEEE Xplore:
Zeeshan Nadir, Michael S. Brown, Mary L. Comer, Charles A. Bouman, “Gaussian Mixture Prior Models for Imaging of Flow Cross Sections from Sparse Hyperspectral Measurements” , 2015 IEEE GlobalSIP Conference, Dec 14-16
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about Joint Composite Detection and Bayesian Estimation: A Neyman-Pearson Approach
- Log in to post comments
The paper considers the composite detection problem where both detection and parameter estimation are of primary interest. Based on a Neyman-Pearson type of formulation, our goal is to find the joint detector and estimator that minimizes a decision-dependent Bayesian estimation risk subject to the detection error probability constraints. The optimal joint solution not only yields lower Bayesian estimation risk compared to the conventional method, which combines the likelihood ratio test and the Bayesian estimator in sequence, but
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Multi-Sensor Generalized Sequential Probability Ratio Test Using Level-Triggered Sampling
- Log in to post comments
This paper investigates the generalized sequential probability ratio test (GSPRT) with multiple sensors. Focusing on the communication-constrained scenario, where sensors transmit one-bit messages to the fusion center, we propose a decentralized GSRPT based on level-triggered sampling scheme (LTS-GSPRT). The proposed LTS-GSPRT amounts to the algorithm where each sensor successively reports the decisions of local GSPRTs to the fusion center.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views