
The IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP) is a flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society. GlobalSIP'15 will be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, December 14-16, 2015. The conference will focus on signal and information processing with an emphasis on up-and-coming signal processing themes. The conference will feature world-class speakers, tutorials, exhibits, and sessions consisting of poster or oral presentations. Outstanding papers will be selected for Best Paper Awards or Best Student Paper Awards; a paper is eligible for a best student paper award if the first author of the paper is a student. IEEE Signal Processing Society and National Science Foundation will provide travel grants to eligible students.
- Read more about Multiresolution Functional Connectivity Analysis Refines Functional Connectivity Networks in Individual Brains
- Log in to post comments
Recent advances in functional connectivity (FC) analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data facilitate the characterization of the brain’s intrinsic functional networks (FC-fMRI). Because the fMRI signal does not provides a perfect representation of neuronal activity, the potential for FC-fMRI to identify functionally relevant networks critically depends upon separating overlapping signals from one another and from external noise. As a step in data preconditioning, researchers often band-pass filter fMRI signals to the range from 0.01 Hz to 0.1 Hz.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views- Read more about Lifetime-aware Networks: It is Not What You Know but Who You Know
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views- Read more about Fast Sparse Recovery via Non-Convex Optimization
- Log in to post comments
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about Informed TDoA-based Direction of Arrival Estimation for Hearing Aid Applications
- Log in to post comments
This presentation deals with estimation of the target sound Direction of Arrival (DoA) for a Hearing Aid System (HAS) which can connect to a wireless microphone worn by a target talker. In this setup, the HAS is "informed" about the almost noise-free content of the target sound via the wireless microphone and can use this information for the DoA estimation. Here, we propose an "informed" DoA estimator based on the Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA) of the target sound at two microphones mounted on the ears of the HAS user---one microphone on each ear.
GlobalSIP.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about Adaptive selection of lag-window shape for linear predictive analysis in the 3GPP EVS codec
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Differential Flux Balance Analysis of Quantitative Proteomic Data on Protein Interaction Networks
- Log in to post comments
Protein fluxes provide a more refined notion of protein abundance than raw counts alone by considering potential channels based on protein interaction networks. We propose a novel method to estimate protein fluxes in a protein interaction network using a linear programming model based on the framework of flux balance analysis.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views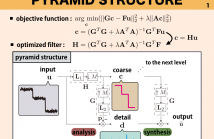
- Read more about Edge Preserving Multiscale Image Decomposition with Customized Domain Transform Filters
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, a multiscale image decomposition method based on domain transform is proposed. The domain transform is a high speed edge preserving smoothing method and can be used to many image processing applications. However, it is highly sensitive to noise. The proposed method is based on filters used in the domain transform but is designed to be robust to noise by employing a multiscale method. An optimization problem is formulated to obtain desired domain- transformed output. As expected, the method can be used to many applications as the domain transform.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 ViewsAn automatic, text-independent speaker verification (SV) system is proposed using Line Spectral Frequency (LSF) features. The state-of-the-art Gaussian Mixture Model with Universal Background Model (GMM-UBM) framework is used for speaker modeling and verification. A score-level fusion based technique is employed in order to extract complementary information from static and dynamic LSF features and improve the noise-robustness of the SV system. In addition, the speaker-discriminative power of different speech zones such as vowels, non-vowels, and transitions are investigated.
 17 Views
17 Views